You spend thousands on employee training only to watch retention numbers drop and skills gaps widen. Without a structured approach, your team forgets up to 90% of what they learn within a week. Scattered resources, unclear objectives, and zero follow through turn your training budget into expensive theater that delivers no measurable results.
A well designed employee training plan changes this. It creates a roadmap that connects learning to business outcomes, tracks progress, and ensures knowledge sticks. Think of it as your blueprint for building competent teams rather than running one off workshops that vanish from memory by Monday morning.
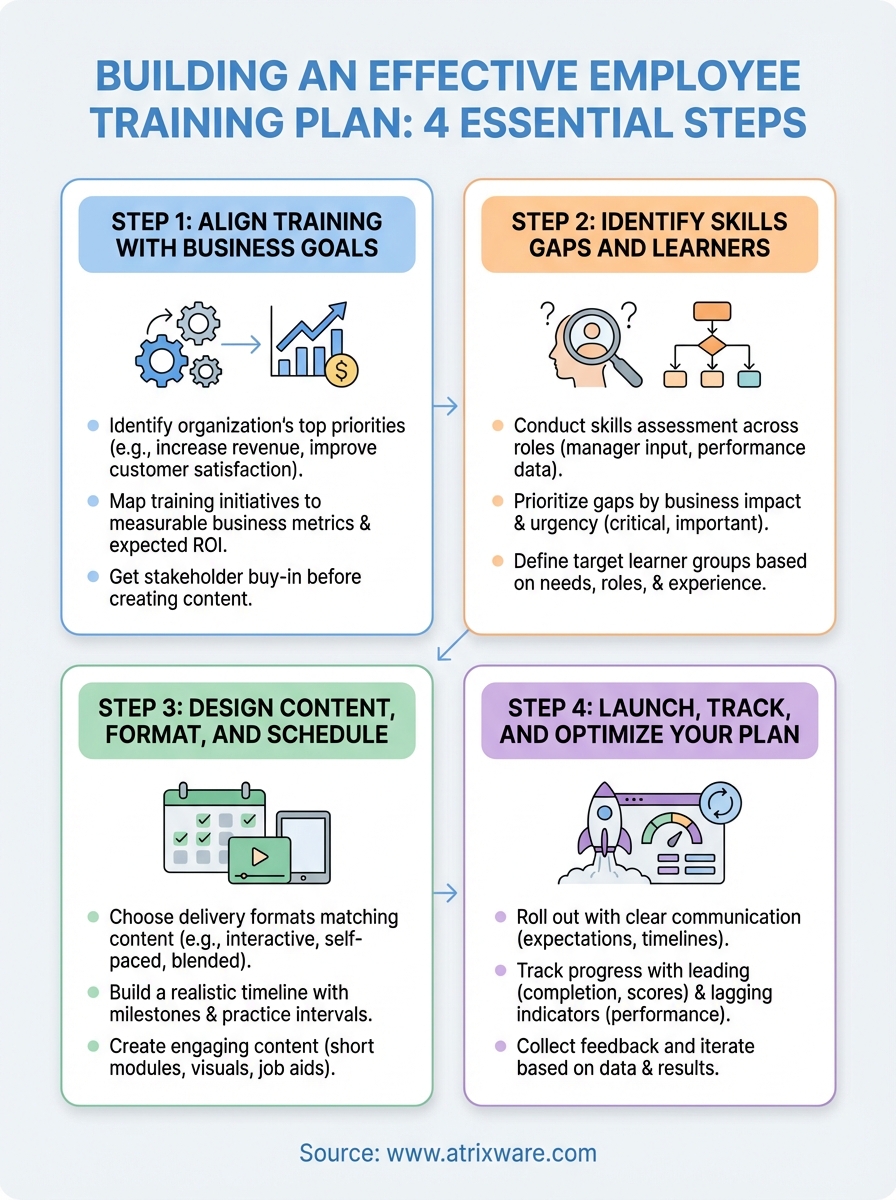
This guide walks you through building an effective training plan from scratch. You’ll discover four essential steps to align training with goals, identify gaps, design engaging content, and optimize results. We’ve included real examples and free templates you can download and customize, so you can start creating plans that actually work.
Why you need an employee training plan
Your training efforts fall flat without a structured employee training plan because random workshops and ad hoc sessions create knowledge that evaporates faster than it forms. Research shows companies waste approximately $774 per participant annually when training lacks structure, follow through, and measurable objectives. You end up repeating the same sessions, answering the same questions, and watching talented people leave because they see no path forward. The frustration compounds when compliance requirements slip through the cracks or critical skills remain underdeveloped despite significant time and budget investments.
The measurable impact on retention and performance
Structured training plans directly affect your bottom line through improved employee retention. Companies that implement comprehensive training programs report significantly higher retention rates because employees value clear development paths. When you document learning objectives, timelines, and success metrics, team members understand exactly what skills they need to advance and how their growth connects to organizational success. This clarity transforms training from a checkbox exercise into a competitive advantage that attracts and keeps top talent.
According to LinkedIn’s research, less than half of managers receive formal management training, creating a massive gap between leadership needs and preparation.
Protection against compliance risks and skill obsolescence
Your organization faces real financial exposure when training lacks documented plans for compliance requirements. Industries regulated by FDA 21 CFR Part 11, GDPR, or other standards require proof of training completion, content versioning, and regular recertification. A formal plan creates this audit trail automatically while ensuring no employee misses mandatory training updates. Beyond compliance, you protect against skill obsolescence by identifying emerging competencies your team needs before competitors do. Strategic training plans help you anticipate market shifts rather than scramble to catch up after falling behind.
Structured plans also eliminate the chaos of duplicate efforts and conflicting information. When multiple departments run separate training initiatives, employees receive inconsistent messages and waste time reconciling contradictory guidance. A unified plan coordinates efforts across teams while making efficient use of subject matter experts.
Step 1. Align training with business goals
Your employee training plan fails before it starts if you cannot draw a direct line between each training initiative and specific business outcomes. Leadership teams cut budgets for programs that feel disconnected from revenue, productivity, or strategic priorities. You need to establish this connection upfront by identifying which company objectives require new or improved employee capabilities and documenting exactly how training will move those metrics. This alignment transforms training from a cost center into an investment that executives understand and support.
Identify your organization’s top priorities
Start by reviewing your company’s strategic plan, quarterly objectives, or annual goals to understand what leadership considers most important right now. Look for objectives that depend on employee performance such as increasing customer satisfaction scores, reducing production errors, expanding into new markets, or launching innovative products. Schedule meetings with department heads to understand their specific challenges and performance gaps that training could address. Ask direct questions about what would need to change for their teams to achieve their targets and which skills or knowledge gaps create the biggest obstacles.
Common business objectives that training supports include improving customer retention through better service skills, accelerating time to productivity for new hires, meeting regulatory compliance requirements, reducing safety incidents, and preparing employees for leadership roles. Your role is to translate abstract goals into concrete learning needs rather than assume you know what training people require.
Map training initiatives to measurable outcomes
Create a simple table that connects each proposed training program to specific business metrics you can track. This mapping forces you to think beyond completion rates and test scores to real world impact.

| Training Initiative | Business Goal | Success Metric | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales methodology workshop | Increase revenue | Average deal size | +15% in Q2 |
| Customer service skills | Improve satisfaction | NPS score | 70+ by June |
| Compliance certification | Meet regulatory requirements | Audit pass rate | 100% certification |
| Leadership fundamentals | Reduce turnover | Manager retention | 90% after 12 months |
Document the expected return on investment by estimating the financial impact of achieving these targets compared to training costs. When you show that a $50,000 training program could prevent $200,000 in compliance penalties or add $500,000 in revenue, approval becomes straightforward.
According to research from management consulting firms, companies with comprehensive training programs that align to business objectives achieve a 415% annualized ROI on their learning investments.
Get stakeholder buy-in before building content
Share your alignment document with executives, department leaders, and finance teams before you invest time creating training materials. Ask them to confirm that the business goals you identified are accurate priorities and that your proposed metrics will actually demonstrate value. This validation prevents you from building elaborate programs that solve problems nobody cares about. Stakeholder involvement at this stage also creates advocates who will champion your training initiatives when you need resources, participation, or ongoing support throughout implementation.
Step 2. Identify skills gaps and learners
You cannot build an effective employee training plan without knowing exactly which skills your team lacks and who needs training most urgently. Many organizations waste resources training people who already possess necessary competencies while overlooking critical gaps that damage performance. A systematic skills gap analysis reveals where to focus your efforts and budget for maximum impact on business results. This step requires gathering data from multiple sources rather than relying on assumptions or subjective opinions about what employees need to learn.
Conduct a skills assessment across roles
Begin by documenting the required competencies for each role in your organization using job descriptions, performance standards, and input from managers. Create a simple matrix that lists roles vertically and essential skills horizontally. Rate current proficiency levels for each employee or team using a consistent scale such as beginner, intermediate, advanced, or expert. You can collect this data through manager assessments, employee self-evaluations, performance review records, certification status, or skills tests depending on what makes sense for your organization.
Look for patterns that indicate widespread gaps versus isolated issues. When an entire department scores low on a critical skill, you need group training. Individual gaps might require mentoring, job shadowing, or targeted coaching instead of formal programs. Review recent performance problems, customer complaints, quality issues, or safety incidents to identify skills deficiencies that have real consequences. These data points provide concrete evidence of training needs rather than vague feelings that something is wrong.
Prioritize gaps by impact and urgency
Not every skills gap deserves immediate attention in your training plan. Evaluate each identified gap using two key criteria: business impact and time sensitivity. High impact gaps directly affect revenue, customer satisfaction, safety, or compliance. Urgent gaps require immediate action due to regulatory deadlines, upcoming product launches, or critical performance issues. Use this simple prioritization framework to decide where to start:

| Priority Level | Impact | Urgency | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Critical | High | High | Train immediately |
| Important | High | Low | Schedule within 90 days |
| Moderate | Low | High | Quick solution or workaround |
| Low | Low | Low | Address when resources allow |
Focus your initial training efforts on critical and important gaps that will deliver measurable improvements to your business goals from Step 1. Document why you are deferring lower priority items so stakeholders understand your strategic choices.
Research shows that 68% of organizations report tangible benefits from upskilling initiatives when they prioritize skills gaps strategically rather than training randomly.
Define your target learner groups
Segment your workforce into logical training cohorts based on shared needs, roles, or experience levels rather than attempting one size fits all programs. Common groupings include new hires in their first 90 days, individual contributors moving into management, technical specialists requiring certification, or customer facing teams needing soft skills development. Each group requires different content depth, delivery methods, and pacing to achieve learning objectives effectively.
Create learner profiles for each target group that specify their current knowledge baseline, preferred learning styles, scheduling constraints, and motivation levels. Understanding whether your audience consists of eager volunteers or reluctant participants required to attend shapes how you design and deliver training. Document the expected class sizes and frequency of training for each group so you can plan resources appropriately.
Step 3. Design content, format, and schedule
Your employee training plan moves from strategy to execution when you make concrete decisions about how learners will consume information and when they will complete each component. This step requires matching training formats to content types, creating realistic timelines that respect employee workloads, and designing materials that people actually remember. Poor choices here lead to abandoned courses, frustrated participants, and zero knowledge retention regardless of how well you completed the previous steps.
Choose delivery formats that match your content
Select training formats based on what employees need to learn rather than what feels easiest to create. Complex technical skills require hands on practice through simulations or live demonstrations, while compliance knowledge transfers effectively through self paced modules with knowledge checks. You waste time and money forcing content into inappropriate formats like turning procedural skills training into slide decks that nobody can apply.

Match these common training types to appropriate delivery methods:
| Content Type | Best Format | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Software skills | Interactive tutorials, screen recordings | Learners practice in real environment |
| Compliance requirements | Self-paced modules with quizzes | Allows individual pacing, provides audit trail |
| Soft skills | Role playing, case studies, group discussion | Requires interaction and feedback |
| Product knowledge | Video demos, job aids, microlearning | Easy to update, accessible on demand |
| Leadership development | Mentoring, workshops, project assignments | Builds through experience over time |
Blend multiple formats within a single program to maintain engagement and reinforce concepts through different modalities. A complete onboarding plan might combine self-paced orientation modules, live department overviews, buddy shadowing sessions, and short video introductions from executives.
Research shows that eLearning boosts retention rates by 25 to 60% compared to traditional classroom training because interactive and self-paced content allows learners to control their experience.
Build a realistic timeline with milestones
Create a schedule that balances business urgency with the time employees actually need to absorb and apply new skills. Cramming too much content into compressed timeframes guarantees surface learning that disappears immediately. Space learning activities over weeks or months with practice intervals between concepts. Your timeline should specify exact dates for each training component, homework assignments, assessments, and check-in meetings so participants can plan accordingly.
Structure your schedule around clear milestones that mark measurable progress toward competency rather than just completion of activities. A 90 day technical training plan might include milestones at day 30 (complete foundational modules), day 60 (pass certification exam), and day 90 (complete supervised project work). Document prerequisites and dependencies so employees understand the sequence and why certain elements must happen before others.
Account for real workplace constraints like peak business periods, existing meeting schedules, time zones for remote teams, and manager availability for coaching sessions. Build buffer time for employees who need additional support without penalizing fast learners who could move ahead.
Create engaging content that drives retention
Design training materials using principles that counteract the forgetting curve where learners lose 70% of knowledge within 24 hours. Break content into digestible chunks of 10 to 15 minutes rather than hour-long lectures. Include frequent knowledge checks, real scenarios from your workplace, and opportunities to apply concepts immediately. Use visuals, job aids, and templates employees can reference later instead of text-heavy slides they will never review again.
Step 4. Launch, track, and optimize your plan
Your employee training plan transforms from document to results when you execute with discipline and continuously improve based on real performance data. Most training initiatives fail not because of poor design but because organizations launch programs and never measure whether they achieve intended outcomes. You need to communicate expectations clearly, monitor progress systematically, and adjust your approach based on what the data reveals about how employees learn and apply new skills in their actual work environment.
Roll out training with clear communication
Announce your training program to all stakeholders at least two weeks before launch with specific details about expectations, timelines, and how participation connects to business goals. Your communication should answer basic questions employees have: why this training matters now, what they will learn, how much time it requires, what happens if they miss sessions, and how completion affects their performance reviews or career advancement. Send calendar invites with exact dates, include preparatory materials employees should review beforehand, and assign clear ownership for tracking attendance and completion.
Create a simple launch checklist that covers technical setup, access permissions, manager briefings, and backup plans:
- Verify all learners have system access and required accounts
- Test all technology components with a pilot group
- Brief managers on their coaching responsibilities during training
- Prepare job aids and reference materials employees can access after training
- Schedule follow-up sessions or office hours for questions
Track progress with meaningful metrics
Monitor both leading indicators that predict success and lagging indicators that measure final outcomes. Leading metrics include login rates, module completion percentages, assessment scores, and time spent in training. These data points tell you whether employees engage with content but not whether they change behavior. Lagging metrics track actual performance improvements such as reduced error rates, faster task completion, higher customer satisfaction scores, or increased sales conversions that you identified in Step 1.

Build a simple dashboard that shows completion status and performance trends:
| Metric | Baseline | Current | Target | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training completion rate | 0% | 78% | 95% | On track |
| Average assessment score | N/A | 87% | 80% | Exceeds |
| Performance metric (specific to goal) | [prior data] | [current data] | [target] | [status] |
Review this data weekly during the training period and monthly after completion to identify employees who struggle and need additional support before they fall too far behind.
Research from the Center for Creative Leadership shows that individuals obtain 70% of their knowledge from job-related experiences, meaning your tracking must extend beyond classroom completion to on-the-job application.
Collect feedback and iterate
Survey participants immediately after training and again 30 to 60 days later to capture both initial reactions and longer term perspectives on relevance and application. Ask specific questions about content clarity, format effectiveness, pacing appropriateness, and whether they use new skills in daily work. Request concrete examples of improvements or obstacles they encountered while applying training concepts. Use this feedback to update materials, adjust timelines, or change delivery formats for future cohorts rather than defending your original design.
Schedule retrospective meetings with managers to discuss which employees demonstrate new competencies and which still struggle despite completing training. These conversations reveal whether your employee training plan addressed the right skills gaps or whether you need to pivot your approach for the next iteration.
Examples and ready to use plan templates
You can accelerate your training program development by starting with proven templates that cover essential components rather than building documents from scratch. These templates provide the structure you need while allowing customization for your specific business context, industry requirements, and learner groups. Download and modify these free employee training plan templates to match your organizational needs and save dozens of hours in the planning phase.
Basic employee training plan template
Your foundational template should capture all critical information in a single document that stakeholders and trainers can reference throughout the program lifecycle. This structure works for most training initiatives regardless of size or complexity.
EMPLOYEE TRAINING PLAN
Program Name: [Specific training initiative]
Business Goal: [From Step 1, linked to measurable outcome]
Target Audience: [Specific roles, departments, or employee groups]
Duration: [Start date to completion date]
Owner: [Person responsible for program success]
SKILLS GAP ADDRESSED:
Current State: [What employees can do now]
Desired State: [What employees need to do after training]
Priority Level: [Critical/Important/Moderate/Low]
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
1. [Specific, measurable objective]
2. [Specific, measurable objective]
3. [Specific, measurable objective]
TRAINING COMPONENTS:
| Component | Format | Duration | Completion Date |
|-----------|--------|----------|-----------------|
| [Module 1] | [Self-paced/Live/Blended] | [Hours/Days] | [Date] |
| [Module 2] | [Self-paced/Live/Blended] | [Hours/Days] | [Date] |
| [Assessment] | [Quiz/Project/Demo] | [Hours/Days] | [Date] |
RESOURCES REQUIRED:
- Materials: [List documents, videos, software access]
- Trainers: [Subject matter experts, instructors]
- Budget: [Estimated costs]
- Technology: [LMS, tools, platforms]
SUCCESS METRICS:
- Completion Rate: [Target percentage]
- Assessment Score: [Minimum passing score]
- Performance Improvement: [Specific business metric from Step 1]
- Feedback Score: [Satisfaction rating target]
FOLLOW-UP PLAN:
- 30-day check-in: [Manager meeting to discuss application]
- 60-day review: [Performance metric measurement]
- 90-day evaluation: [Final assessment and program adjustment]
Specialized templates by training type
Different training purposes require modified templates that emphasize specific elements relevant to that context. A new hire onboarding plan needs more detail about company culture and systems access, while compliance training demands strict documentation of completion dates and version control for audit requirements. Technical skills training templates should include hands-on practice components and certification tracking, whereas leadership development plans benefit from mentoring assignments and stretch project definitions.
According to industry research, 76% of employees are more likely to stay with companies that offer structured, ongoing training opportunities, making your template selection and customization a retention strategy.
Download role-specific templates for onboarding programs, compliance certification, sales methodology, customer service skills, and software proficiency training from major LMS providers who publish free resources. Modify the assessment criteria, timeline structure, and follow-up intervals to match your organization’s pace and culture while keeping the core framework intact.
Final thoughts
Your employee training plan succeeds when you connect learning directly to business outcomes, identify real skills gaps, design engaging content, and track meaningful results. The templates and frameworks in this guide eliminate the guesswork and wasted effort that plague most training initiatives. You now have the structure to build programs that employees actually complete and apply in their daily work rather than forgetting within days.
The right technology platform transforms your training plan from a static document into a dynamic system that tracks progress, automates reminders, and proves ROI to stakeholders. An LMS handles the administrative burden while you focus on content quality and learner engagement. Take our LMS readiness quiz to assess where you stand in the evaluation process and discover which features matter most for your specific training needs. Understanding your readiness level helps you make informed decisions about tools and timing rather than rushing into expensive platforms before your organization is prepared to use them effectively.
