Your workforce just doubled. New regulations went into effect. Remote employees need training across three continents. You realize your current compliance training program cannot keep up. Manual tracking breaks down. Course assignments get missed. Audit trails become incomplete. The risk grows with every new hire and regulatory update.
The solution is building a compliance training system that scales without adding administrative burden. You need standardized content, automated workflows, and centralized tracking that works whether you have 50 employees or 5,000. When designed correctly, compliance training becomes a repeatable process instead of a constant fire drill.
This guide walks you through four practical steps to implement compliance training at scale. You will learn how to audit your requirements, design a scalable curriculum, select the right technology and content partners, and establish measurement systems that improve over time. By the end, you will have a clear roadmap for building compliance training that grows with your organization.
Why scalable compliance training matters
Your compliance training program works fine at 100 employees. Assignments happen manually, you track completions in spreadsheets, and your HR team can handle the occasional reminder. But when you reach 500 or 1,000 employees, that same approach collapses. Manual processes cannot scale without exponentially increasing your administrative workload. The compliance gaps that were manageable risks become audit failures and legal liabilities.

The cost of manual compliance management
Manual compliance training creates invisible costs that multiply as you grow. Your HR team spends hours each week chasing incomplete training, sending reminder emails, and updating spreadsheets. When auditors request proof of training, your team scrambles to compile records from multiple sources. You discover gaps in training history, missing completion certificates, and employees who slipped through the cracks entirely. Each new hire adds administrative burden, and each new regulation requires manual reassignment across your entire workforce.
Organizations with manual compliance systems spend 3-5 times more hours on administrative tasks than those with automated systems.
How scale changes training requirements
Scale transforms compliance training from a simple task into a complex orchestration problem. You need different training paths for different roles, automated assignment based on job function, and tracking that captures every completion, attempt, and certification expiration. When you operate across multiple locations or countries, you must deliver region-specific compliance training for employees while maintaining consistent tracking. Your system needs to handle simultaneous course updates, version control, and automatic reassignment when regulations change. Manual methods cannot manage this complexity.
The stakes increase with scale. Larger workforces mean higher regulatory exposure and greater financial penalties for non-compliance. A single missed training requirement in a company of 50 might cost thousands in fines. That same gap in a company of 5,000 could cost millions. Audit readiness becomes critical when you need to produce training records for hundreds or thousands of employees within days. Scalable systems provide instant reporting, complete audit trails, and proof of compliance that withstands regulatory scrutiny.
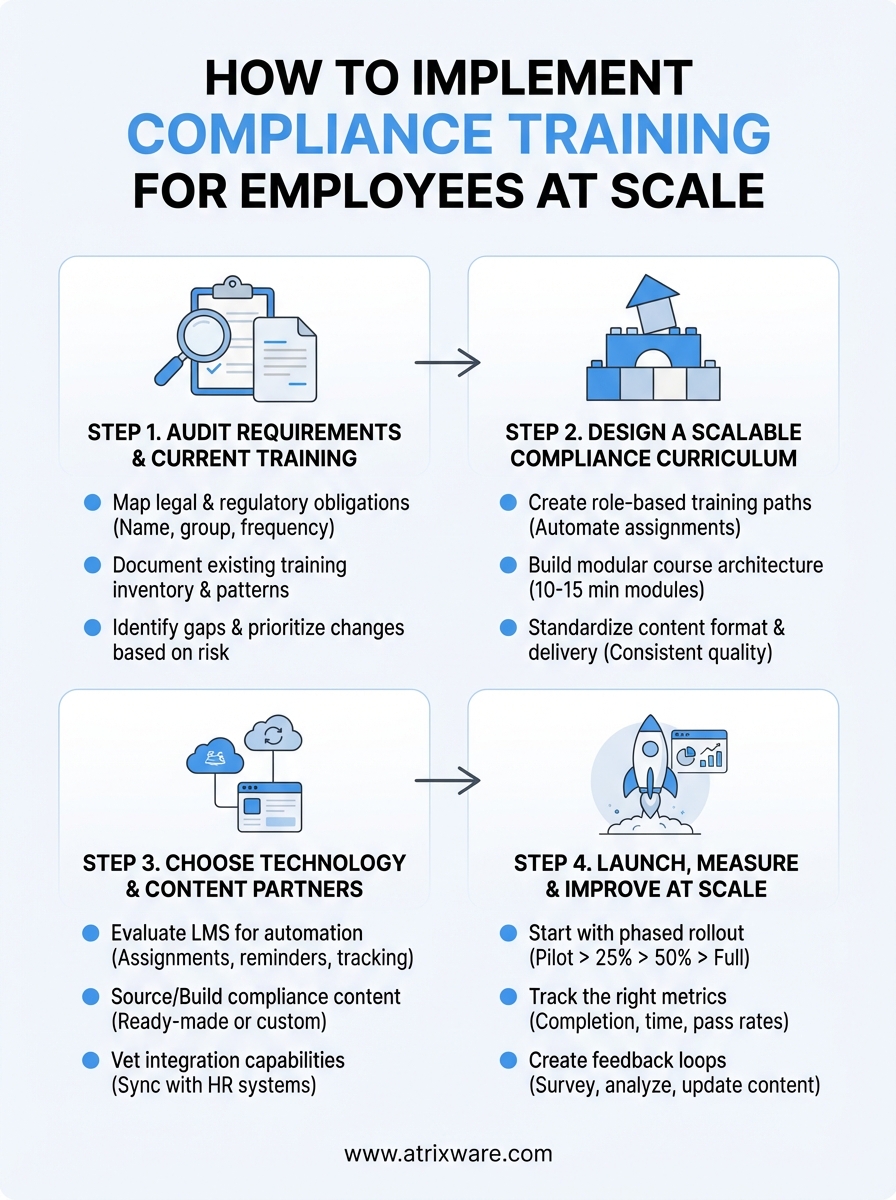
Step 1. Audit requirements and current training
You cannot scale what you do not understand. Your first step requires complete visibility into your compliance obligations and an honest assessment of your current training program. This audit reveals exactly what training you must deliver, who needs it, and where your existing system falls short. Without this foundation, you will build a scalable system that automates the wrong processes and misses critical requirements.
Map your legal and regulatory obligations
Start by creating a comprehensive list of every compliance requirement that applies to your organization. Review federal regulations like OSHA, HIPAA, or FDA standards that govern your industry. Check state and local laws that add requirements based on your business locations. Document the specific training mandates for each regulation, including who must complete the training, how often, and what proof you need to maintain.

Your audit should capture five critical details for each requirement: the regulation name and citation, the employee groups it applies to, the required training frequency, the documentation standard, and the penalty for non-compliance. Create a simple table to track this information and make it easy to reference during curriculum design. Include requirements from professional certifications or industry standards your organization follows, even when not legally mandated. Your audit becomes your compliance roadmap that guides every subsequent decision.
Organizations that document compliance requirements in a central reference reduce audit preparation time by 60% and catch gaps before regulators do.
Document your existing training inventory
Catalog every compliance course you currently deliver, regardless of format. List instructor-led sessions, online modules, PDF documents, and video training. Record the course title, the compliance requirement it addresses, the typical completion time, and the current delivery method. Track who has completed each course and when, even if your records are incomplete or scattered across multiple systems.
This inventory reveals patterns in your current approach. You might find duplicate courses covering the same requirement, outdated content that no longer matches regulations, or critical topics with no formal training at all. Evaluate each course for quality and effectiveness. Identify which courses can scale to larger audiences without modification and which need rebuilding from scratch.
Identify gaps and prioritize changes
Compare your requirements list against your training inventory to find missing courses, outdated content, and incomplete tracking. Flag any requirement where you lack formal training, cannot prove completion, or rely on manual processes that break at scale. Prioritize gaps based on regulatory risk, focusing first on requirements with the highest penalties or shortest compliance deadlines.
Build a priority matrix that scores each gap on two dimensions: regulatory risk and implementation effort. Address high-risk, low-effort gaps immediately. Plan for high-risk, high-effort gaps in your next phase. This prioritization prevents you from building a perfect system for low-risk requirements while leaving critical compliance gaps unaddressed.
Step 2. Design a scalable compliance curriculum
Your curriculum architecture determines how easily you can scale compliance training for employees across your organization. A scalable design uses modular courses, role-based assignments, and standardized formats that work whether you have 100 or 10,000 learners. Build your curriculum around courses that can be assigned automatically based on employee data, updated independently, and tracked consistently. This structure eliminates the manual work that breaks down at scale and creates a foundation for automated compliance management.
Create role-based training paths
Design training paths that automatically assign the right courses based on job function, department, and location. Create a matrix that maps each compliance requirement to specific employee roles. Your matrix should include columns for the role name, required courses, training frequency, and trigger conditions for assignment.

Here is a basic structure for your role-based matrix:
| Role/Department | Required Courses | Frequency | Assignment Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Employees | Workplace Safety, Anti-Harassment, Data Security | Annual | Day 1 of employment |
| Managers | All Employee courses + Leadership Ethics, Performance Management | Annual | Upon promotion to manager |
| Healthcare Staff | HIPAA Privacy, HIPAA Security, Bloodborne Pathogens | Annual | Day 1 in clinical role |
| Sales Team | Anti-Bribery, Export Controls, Sales Ethics | Annual | Day 1 in sales role |
| California Employees | All required courses + CA Sexual Harassment Prevention | Biennial | Assignment to CA location |
Role-based paths reduce administrative burden by automating 90% of course assignments. Your system assigns courses when employees join, change roles, or reach certification expiration dates. You eliminate manual tracking and ensure every employee receives their required training without HR intervention.
Build modular course architecture
Break complex compliance topics into discrete, reusable modules that you can combine for different audiences. Design each module to cover one specific concept or requirement in 10-15 minutes. Modular courses let you update content without rebuilding entire programs and allow employees to complete training in short sessions that fit their workflow.
Your module structure should follow a consistent template that includes a clear learning objective, core content, real-world scenarios, a knowledge check, and a summary. Create a master list of approved modules organized by topic area. When regulations change, you update only the affected modules and automatically reassign them to relevant employees. This approach scales because you maintain one module that serves multiple training paths instead of duplicating content across separate courses.
Modular course design reduces content maintenance time by 70% and allows organizations to respond to regulatory changes within days instead of months.
Standardize content format and delivery
Establish strict standards for course format, length, and assessment that every module must follow. Set maximum course lengths, define required elements like introductions and summaries, and specify minimum passing scores. Standardization makes courses interchangeable and ensures consistent quality regardless of who creates the content or which vendor provides it.
Document your standards in a content creation guide that includes slide templates, script formats, assessment requirements, and accessibility specifications. Your guide should specify file formats, video resolution, audio quality, and supported media types. Standards ensure that every course works in your learning management system, tracks completion correctly, and meets accessibility requirements. When you source content from multiple vendors or create it internally, standards prevent integration problems that slow deployment and create tracking gaps.
Step 3. Choose technology and content partners
Your technology and content decisions directly impact how well your compliance training scales. You need a learning management system that automates assignments and tracking while sourcing compliance content that meets your regulatory requirements. The right combination eliminates manual work and ensures your compliance training for employees stays current as regulations change. Poor choices here create bottlenecks that prevent scaling, forcing you back into manual processes that collapse under growth.

Evaluate LMS platforms for automation
Select an LMS that automates course assignments based on employee data from your HR system. Your platform must trigger training when employees join, change roles, or reach certification expiration dates. Look for automatic notification systems that send reminders without manual intervention and escalation workflows that alert managers when employees miss deadlines.
Core automation features you need include:
- Role-based assignment rules that map job titles or departments to required courses
- Scheduled reassignment for annual or periodic compliance renewal
- Completion tracking with tamper-proof audit trails and digital certificates
- Reporting dashboards that show compliance status by department, location, or regulation
- API integration to sync employee data automatically with your HRIS
Your LMS should generate compliance reports instantly instead of requiring manual data compilation. Test each platform’s reporting before committing. Request a demo where you can view completion rates by regulation, identify non-compliant employees, and export audit-ready documentation. Platforms that cannot produce these reports in seconds will not scale effectively.
Organizations using LMS platforms with automated assignment reduce compliance administration time by 85% compared to manual tracking methods.
Source or build compliance content
Decide whether to purchase ready-made courses, create custom content, or combine both approaches. Off-the-shelf courses from established providers cost less and launch faster but may not address your specific policies or procedures. Custom content fits your exact needs but requires significant time and budget to develop and maintain.
Evaluate content providers based on regulatory accuracy, update frequency, and format compatibility. Ask how often they refresh courses when regulations change and whether updates are included in your licensing fee. Verify that courses meet your jurisdiction’s specific requirements, not generic versions that might miss state or local mandates. Request sample courses to assess quality, length, and engagement before purchasing.
Vet integration capabilities
Your LMS must connect directly to your HR system, identity provider, and other core platforms. Integration eliminates duplicate data entry, ensures employees have current role assignments, and maintains accurate training records. Look for pre-built connectors to major HRIS platforms or open APIs that your IT team can use for custom integration.
Test critical integration points before selecting a platform. Verify that employee data syncs automatically when roles change, terminated employees lose access immediately, and completion data flows back to your HR system. Ask vendors for technical documentation and integration timelines during your evaluation. Platforms that require extensive custom development to integrate will slow your deployment and increase costs beyond initial licensing fees.
Step 4. Launch measure and improve at scale
Your launch strategy determines whether your compliance training program succeeds or stalls. You need a phased approach that starts with a pilot group, validates your technology and content, and expands systematically across your organization. Rushing to deploy compliance training for employees company-wide creates chaos when you discover configuration errors, content gaps, or technical issues at scale. Launch deliberately with built-in measurement that tells you exactly how your program performs and where it needs improvement.
Start with a phased rollout
Begin with a pilot group of 50-100 employees representing different departments, locations, and roles. This pilot tests your assignment rules, completion tracking, and notification systems before you commit to full deployment. Select pilot participants who will provide honest feedback about user experience and help you identify problems that might not surface in testing environments.
Your rollout should follow this phased approach:
| Phase | Audience Size | Duration | Success Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pilot | 50-100 employees | 2-4 weeks | 95% completion rate, no technical issues, positive user feedback |
| Phase 1 | 25% of workforce | 4-6 weeks | Automated assignments work correctly, reporting validates data accuracy |
| Phase 2 | Next 50% of workforce | 6-8 weeks | Support requests remain manageable, completion rates match pilot |
| Phase 3 | Remaining workforce | 4-6 weeks | All automation functions correctly at full scale |
Document every issue during your pilot and resolve it before expanding to the next phase. Test that your LMS handles increased load without performance degradation. Validate that completion data flows correctly to your HR system and audit reports generate accurately. Each phase proves your system works at the next level of scale.
Organizations that use phased rollouts reduce implementation failures by 80% and achieve full compliance 40% faster than those that launch to everyone simultaneously.
Track the right metrics
Monitor completion rates by role, department, and location to identify patterns in non-compliance. Your metrics should reveal whether specific groups struggle with training, whether certain courses have technical issues, or whether your notification strategy fails to reach employees. Track time-to-completion to understand how long employees need to finish courses and whether your deadlines are realistic.
Focus on these core metrics weekly:
- Overall completion rate: percentage of assigned training completed on time
- Past-due training: number and percentage of employees with overdue assignments
- Average time-to-complete: days from assignment to completion by course
- First-attempt pass rates: percentage passing assessments without retakes
- Support ticket volume: help desk requests related to training access or content
Set up automated dashboards that update daily so you can spot problems immediately instead of discovering them during quarterly reviews.
Create feedback loops
Collect employee feedback immediately after course completion through short surveys that ask about content clarity, technical issues, and time investment. Your survey should include both rating scales and open-ended questions that reveal specific problems. Keep surveys to three questions maximum to ensure high response rates.
Build a quarterly review process that analyzes feedback patterns and completion data to identify courses needing updates or replacement. When regulations change, update affected modules and automatically reassign them to employees who completed older versions. Track which courses generate the most support requests and prioritize them for content revision or technical fixes. Your measurement system should feed directly into content improvement decisions that make training more effective with each iteration.
Make compliance training scalable
Your compliance training program scales when you automate assignments, centralize tracking, and standardize content. The four steps you covered transform manual processes into systematic workflows that grow with your workforce. Audit your requirements to understand exactly what training you must deliver and where current gaps expose you to risk. Design a modular curriculum that assigns courses based on employee roles and adapts when regulations change. Select technology that integrates with your existing systems and eliminates duplicate data entry. Launch in phases that validate your approach before expanding company-wide.
Scalability requires ongoing maintenance. Review your compliance training for employees quarterly to catch regulatory changes before they create gaps. Update content modules independently without rebuilding entire programs. Monitor your metrics to identify courses that confuse employees or create bottlenecks. Your system improves through continuous measurement and refinement.
Axis LMS provides the automation, integration, and reporting infrastructure that makes enterprise compliance training manageable at any scale.
