Training teams across organizations face a common challenge: delivering consistent, trackable learning experiences without drowning in spreadsheets and manual follow-ups. That’s where a Learning Management System steps in. But how does an LMS work, exactly? Understanding the mechanics behind this technology helps you evaluate whether it’s the right solution for your training goals.
An LMS handles everything from hosting course content to tracking who completed what, and when. It automates notifications, generates reports, and creates a centralized hub where learners access materials on their own schedule. For administrators, this means less time chasing down completions and more time focusing on content quality and learner engagement.
This guide breaks down the core features, typical workflows, and tracking capabilities that make an LMS function. Whether you’re considering your first system or evaluating a switch, you’ll walk away with a clear picture of what happens under the hood. At Atrixware, we’ve built Axis LMS to address these exact needs, so the insights here come from real-world experience helping organizations streamline their training programs.
Why organizations use an LMS
Organizations adopt an LMS when manual training processes become bottlenecks. Tracking who completed which module through spreadsheets creates errors, outdated course materials float around email attachments, and compliance audits turn into multi-week scrambles. These pain points drive teams to seek a system that centralizes everything in one place. Understanding how does an LMS work starts with recognizing the problems it solves, not just the features it offers.
The shift to remote and hybrid work accelerated LMS adoption across industries. When you can’t gather everyone in a conference room, you need a platform that delivers training consistently regardless of location or time zone. Companies also recognize that effective training directly impacts performance metrics. Better-trained employees make fewer mistakes, serve customers more effectively, and adapt faster when processes change.
To centralize training content and eliminate version control chaos
Before implementing an LMS, your training materials likely live in multiple places. Instructor presentations sit on individual laptops, policy documents hide in shared drives with unclear naming conventions, and nobody knows which version is current. When someone updates a procedure, you spend hours notifying everyone and hoping they find the right file.
An LMS becomes your single source of truth for all learning materials, ending the guesswork around which content is current.
You upload materials once, and every learner sees the same version instantly. When regulations change or you improve a training module, you update it in one location. The system immediately reflects those changes for anyone accessing that content, whether they’re taking the course for the first time or revisiting it for a refresher.
To track compliance requirements automatically
Regulatory compliance creates significant administrative burden without an LMS. You need to prove specific employees completed required training before certain dates, track certification expiration dates, and document everything for auditors. Spreadsheets fail when you scale beyond a handful of employees, and manual tracking consumes hours each week.
An LMS automates these requirements entirely. The system logs every completion, tracks due dates, and sends automatic reminders before certifications expire. When an auditor requests proof of training, you generate a comprehensive report in minutes instead of piecing together records from multiple sources. For industries like healthcare or finance, this capability alone justifies the investment.
To scale training without multiplying costs
Traditional training requires instructors, physical space, travel expenses, and materials for every session. Growing your team means repeating these costs with each new hire or when rolling out company-wide initiatives. The expense scales linearly with your headcount, creating budget pressure as you expand.
An LMS breaks this pattern. You create a course once, and thousands of employees can take it without additional instructor time or venue costs. Whether you’re onboarding five new hires or five hundred, the system delivers consistent training at the same base cost. This economic advantage becomes more significant as your organization grows, particularly for companies with high turnover or seasonal workforce fluctuations.
To create consistent learning experiences across locations
Companies with multiple offices, franchises, or distributed teams face a quality control challenge. Different locations develop their own training approaches, leading to inconsistent knowledge and performance gaps. When a customer interacts with your brand in different cities, they should receive the same level of service regardless of which employee helped them.
Your LMS ensures every location follows identical training protocols. New hires in California receive the same onboarding experience as those in New York or remotely. You maintain brand standards and operational procedures uniformly across your entire organization, eliminating the "that’s how we’ve always done it here" problem that creates friction and inefficiency.
The main parts of an LMS and what each does
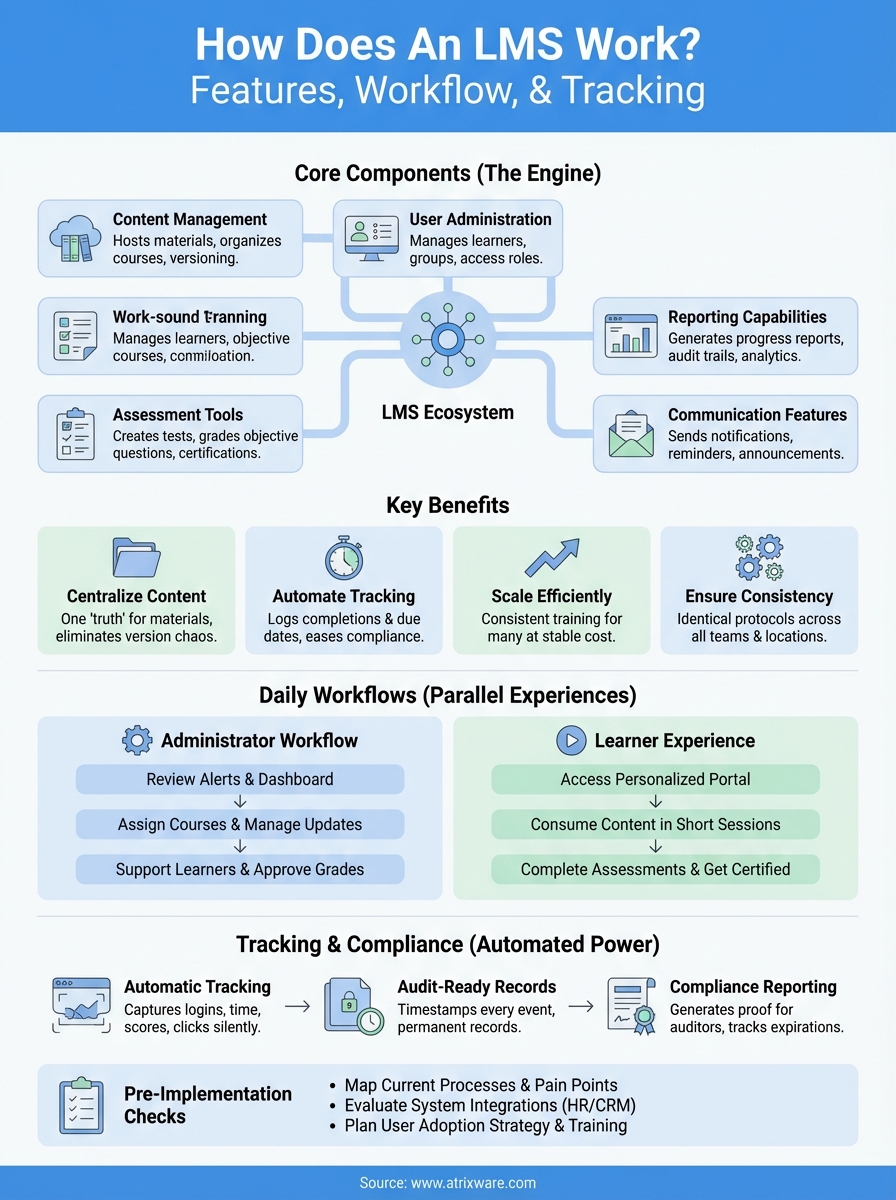
Understanding how does an LMS work requires breaking down its core components and their specific functions. Each part handles distinct responsibilities that together create a complete training ecosystem. The system architecture typically includes five essential elements: content management, user administration, assessment tools, reporting capabilities, and communication features. These components interact to automate workflows that previously required manual coordination.

Content management and delivery system
The content management layer serves as your digital library for all training materials. You upload videos, documents, SCORM packages, presentations, and interactive modules into this repository. The system organizes these assets into structured courses with defined sequences, prerequisites, and completion criteria. Learners access this content through their portal, which presents materials in the order you’ve designed for optimal learning progression.
This component also handles content versioning and access permissions. When you update a training module, the system maintains previous versions while immediately serving the current content to active learners. You control which user groups see specific courses, ensuring sensitive information reaches only appropriate audiences within your organization.
User management and access control
Your LMS maintains a complete database of every learner in your system, tracking their profile information, assigned courses, and progress status. Administrators create individual accounts or import entire rosters from HR systems through integrations. The platform assigns users to groups based on department, location, role, or any custom criteria relevant to your training structure.
Access control determines what each user can see and do within the system, creating personalized experiences based on their role and training needs.
Permission levels separate administrators, instructors, and learners with different capabilities at each tier. Administrators configure the system and assign training, instructors create and manage course content, and learners access their assigned materials. This hierarchy prevents confusion and maintains security boundaries throughout your training environment.
Assessment and evaluation tools
The assessment engine creates tests, quizzes, surveys, and assignments that measure knowledge retention and skill application. You build questions using multiple formats including multiple choice, true/false, fill-in-blank, and essay responses. The system automatically grades objective questions and routes subjective answers to instructors for manual evaluation, saving significant time while maintaining assessment quality and consistency.
These tools also support certification workflows and competency tracking. When learners pass assessments meeting your threshold scores, the LMS automatically awards certificates and updates their training records. You establish passing scores, attempt limits, and time restrictions that enforce your quality standards across all evaluations.
How an LMS works day to day for admins and learners
The daily operation of an LMS creates two distinct but interconnected experiences. Administrators spend their time managing the system, assigning courses, and monitoring progress, while learners focus on consuming content and completing their required training. Understanding how does an Lms work in practice means examining these parallel workflows and how they interact to create a functioning training ecosystem.
Administrator daily workflow
Your day as an LMS administrator starts by reviewing dashboard notifications and alerts. The system flags overdue assignments, upcoming certification expirations, and learners who attempted courses but haven’t finished. You prioritize these alerts based on urgency, reaching out to employees approaching compliance deadlines or escalating persistent non-completion issues to their managers.
Administrators spend most of their time on strategic decisions about course assignments and content updates rather than chasing down individual completions.
You assign new courses to individuals or groups based on role changes, new hires, or updated requirements. When someone gets promoted, you add their new job-specific training with appropriate due dates and prerequisites. If regulations change, you update affected courses and re-assign them to relevant employees, setting new completion deadlines that meet your compliance windows.
Throughout the day, you respond to learner questions about technical issues or content clarification. The system’s communication tools let you send targeted messages to specific groups or broadcast announcements about upcoming training initiatives. You also review instructor feedback on assessment submissions that require manual grading, approving or rejecting completions based on the quality of submitted work.
Learner daily experience
Learners log into their portal and immediately see a personalized dashboard showing assigned courses, progress bars, and upcoming deadlines. The interface highlights courses due soonest at the top, helping you prioritize which training to tackle first. You click into a course and pick up exactly where you left off during your last session, with the system remembering your progress through each module.
Your learning happens in short sessions that fit around your regular work responsibilities. You might complete a 10-minute video during lunch, then return later to finish the associated quiz. When you pass an assessment, the system instantly updates your completion status and sends you a certificate if the course awards one. Notifications remind you about incomplete courses approaching their deadlines, preventing last-minute rushes or missed requirements.
How LMS tracking, reporting, and compliance work
The tracking and reporting capabilities represent the most powerful automation features of any LMS. Every action a learner takes gets logged automatically into the database, creating a complete audit trail without manual intervention. When someone starts a course, completes a module, passes an assessment, or downloads a certificate, the system records that event with timestamps and user identification. This automated tracking answers the question of how does an LMS work at a fundamental level, transforming scattered training activities into structured, searchable data.
![]()
Automatic tracking behind the scenes
Your LMS captures dozens of data points for every training interaction. The system tracks login frequency, time spent on each page, quiz attempts and scores, video completion percentages, and navigation patterns through course content. This granular tracking happens without learner or administrator intervention, running silently in the background while creating a comprehensive record of all learning activities.
The platform timestamps every significant event, establishing clear documentation of when training occurred. You can prove exactly when an employee started required compliance training, how long they spent on each module, and which date they completed the final assessment. This level of detail becomes critical during audits or when investigating incidents related to training gaps.
Generating reports for different stakeholders
Administrators access pre-built report templates that answer common questions instantly. You generate completion reports showing which employees finished their assigned courses, progress reports tracking learners currently working through materials, and assessment score reports revealing knowledge gaps. The system formats these reports for export to spreadsheets or PDF documents that you share with management.
Custom report builders let you filter data by department, location, time period, or any combination of criteria that matters to your organization’s specific needs.
Your executive team receives high-level dashboards showing completion rates and training costs per employee, while department managers get detailed views of their team’s progress. Compliance officers export audit-ready reports proving regulatory requirements were met within specified timeframes.
Meeting compliance and audit requirements
The LMS maintains permanent records that survive employee turnover and system upgrades. When an auditor requests proof that specific training occurred three years ago, you retrieve those records instantly rather than reconstructing them from paper files. The system also enforces recertification schedules automatically, requiring employees to retake courses before their credentials expire.
What to check before you choose or roll out an LMS
Selecting the right LMS requires honest assessment of your specific needs rather than getting distracted by feature lists. Many organizations purchase systems packed with capabilities they’ll never use while missing critical functions that would have solved their actual problems. Before evaluating vendors or implementing a platform, you need clarity on several foundational elements that determine whether a system will succeed or create new headaches.
Your current training processes and pain points
Start by documenting exactly how training happens today in your organization. Map out every step from identifying training needs through measuring results and maintaining records. You’ll discover bottlenecks, redundant tasks, and manual processes consuming excessive time. These pain points become your priority requirements list when evaluating systems.
Interview the people who deliver and consume training daily to understand their frustrations. Training coordinators might spend hours chasing completion confirmations, while learners struggle finding the materials they need. Your sales team might need mobile access for field training, or your compliance officer requires specific audit trail features. These insights prevent choosing a system that solves theoretical problems while ignoring your real challenges.
Integration capabilities with existing systems
Your LMS doesn’t exist in isolation. You need seamless data flow between your HR system, CRM platform, and other business tools. When someone joins your company, their user account should create automatically in your LMS without manual data entry. Understanding how does an LMS work within your existing technology ecosystem determines whether implementation succeeds or creates integration nightmares.
Check whether the platform offers pre-built connectors for your specific systems or requires custom API development that increases costs and implementation time.
Review your authentication requirements carefully. Single sign-on eliminates the password fatigue that reduces learner engagement, while automated user provisioning saves hours of administrative work each week. Systems lacking these capabilities force you into workarounds that undermine efficiency gains you expected from the platform.
User adoption and change management strategy
Technical capabilities matter less than actual usage rates among your target audience. You need an implementation plan addressing resistance and training gaps before launch day. Identify champions within each department who understand the platform’s value and can support their colleagues through the transition.
Budget time for administrator training that goes beyond basic system navigation. Your team needs to understand reporting capabilities, troubleshooting common issues, and configuring features that match your workflows. Plan phased rollouts that test the system with smaller groups before company-wide deployment, allowing you to refine processes and address concerns while stakes remain low.
Conclusion
Understanding how does an LMS work helps you evaluate whether this technology fits your organization’s training needs. The system centralizes content delivery, automates tracking, and generates compliance reports without manual intervention. These capabilities transform scattered training processes into streamlined workflows that scale with your organization’s growth.
The components we covered (content management, user administration, assessments, reporting, and communication tools) work together to eliminate manual tasks that consume administrative time. You gain visibility into who completed what training, when certification deadlines approach, and where knowledge gaps exist across your teams. This visibility drives better decisions about training investments and resource allocation throughout your organization.
Your next step depends on where you stand in the evaluation process. If you’re still weighing whether an LMS makes sense for your team, our LMS readiness quiz helps you assess your current situation and identify specific features that address your training challenges. The results show exactly where you are in the decision process.
