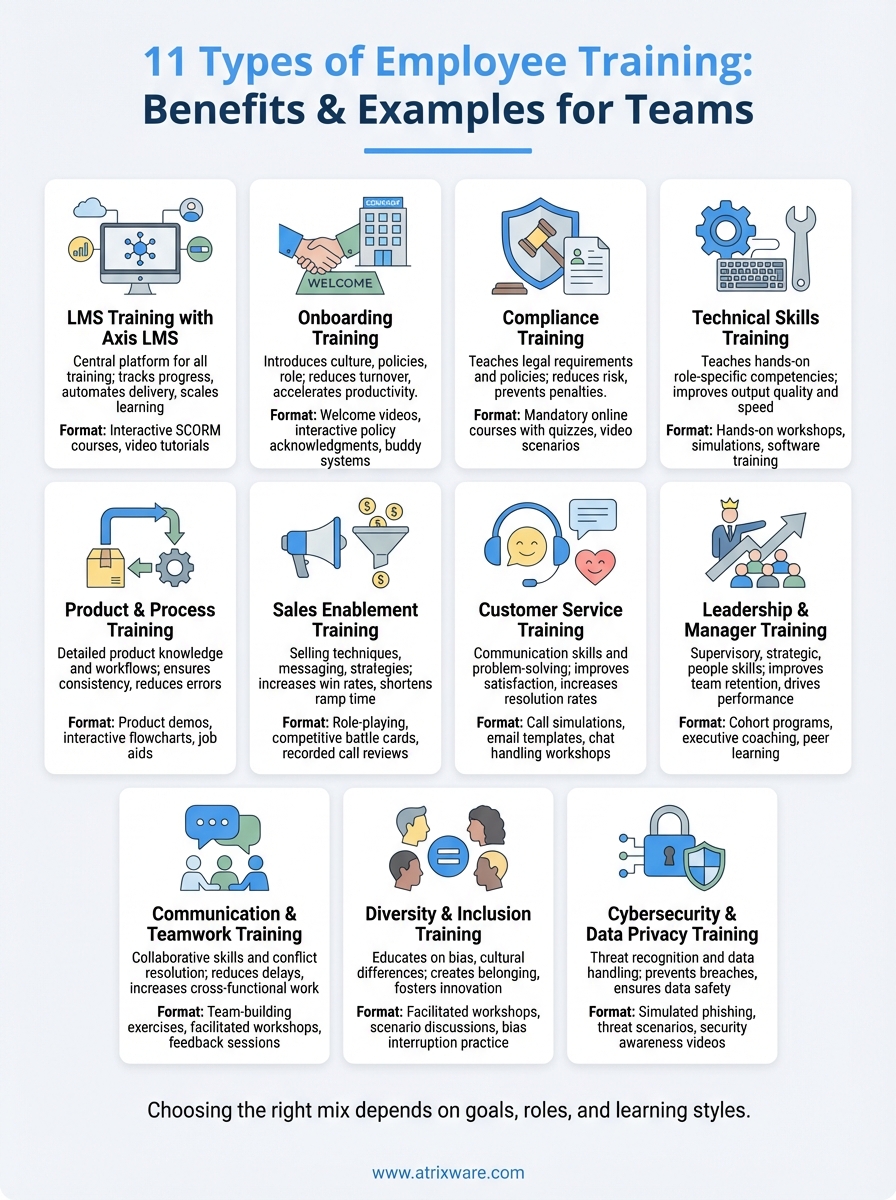
Every organization trains its people, but not every organization does it well. The difference often comes down to choosing the right types of employee training for specific goals, roles, and learning styles. When you match the training method to the need, employees retain more, perform better, and actually engage with the material.
The challenge? There are dozens of training approaches out there, and picking the wrong one wastes time and budget while leaving skill gaps wide open. Whether you’re building out a new hire program, addressing compliance requirements, or upskilling your sales team, understanding your options is the first step toward building something that works.
This guide breaks down 11 proven training types used by organizations of all sizes. For each one, you’ll find practical benefits, real-world examples, and guidance on when it makes the most sense. At Atrixware, we’ve spent years helping businesses deliver effective training through Axis LMS, so we’ve seen firsthand what drives results and what falls flat. Use this as your reference point for designing training programs that actually move the needle.
1. LMS training with Axis LMS
A Learning Management System (LMS) serves as your central platform for delivering, tracking, and managing all other types of employee training. Rather than being a single training type, an LMS like Axis LMS becomes the foundation that supports your entire learning ecosystem. It lets you house compliance courses, onboarding materials, technical certifications, and soft skills programs in one searchable location. You can automate notifications, track completion rates, and generate reports that show exactly who learned what and when.

What it covers
LMS-based training covers virtually every learning need across your organization. You can deliver compliance modules, product knowledge courses, skills certifications, and even virtual classroom sessions through the platform. The system handles course creation, learner enrollment, progress tracking, and certification management in one interface. This eliminates the need to juggle multiple tools or spreadsheets, which means less administrative overhead for your training team.
When to use it
You should deploy an LMS when your training needs scale beyond manual tracking. If you’re onboarding multiple employees simultaneously, managing recurring compliance deadlines, or delivering training to geographically dispersed teams, an LMS solves those challenges. Organizations also turn to LMS platforms when they need audit trails for regulatory compliance or when they want to sell training content to external customers and partners.
Benefits for teams
Teams gain immediate access to training materials on demand, which means they can learn at their own pace rather than waiting for scheduled sessions. Managers get real-time visibility into completion rates and assessment scores, so they can identify struggling learners before small gaps become big problems. The system also reduces your training costs by eliminating travel expenses and allowing you to reuse high-quality content across multiple departments and locations.
An LMS transforms scattered training efforts into a unified, measurable program that grows with your business.
Examples and formats
Common formats include interactive SCORM courses, video tutorials, quizzes, virtual instructor-led sessions, and downloadable resources. You might build a new hire orientation that combines videos, knowledge checks, and policy acknowledgments. Sales teams often access product training modules with simulations and role-playing exercises. Leadership development programs use a mix of self-paced content and live webinars to build management skills over time.
How to measure results
Track completion rates, assessment scores, time to competency, and certification status through built-in reporting dashboards. Most LMS platforms let you set up automated reports that show training gaps by department, role, or location. You can also measure business impact by comparing performance metrics before and after training interventions, such as sales numbers after product training or incident rates following safety courses.
2. Onboarding training
Onboarding training introduces new hires to your organization’s culture, policies, systems, and role expectations during their first days or weeks. This type of employee training sets the foundation for long-term success by helping employees understand how your company operates and where they fit in. Strong onboarding reduces early turnover, accelerates productivity, and creates a positive first impression that shapes employee engagement for years to come.
What it covers
Your onboarding program typically includes company history, mission and values, organizational structure, and key policies like benefits, code of conduct, and workplace safety. It also covers role-specific responsibilities, team introductions, system access, and initial tasks that help new hires start contributing quickly. Many programs blend administrative requirements with cultural immersion to build both competence and connection.
When to use it
You deploy onboarding training every time you hire a new employee, regardless of their experience level or position. Even senior leaders need context about your specific culture and processes. Some organizations also use refresher onboarding when employees transfer to new departments or take on significantly different roles.
Benefits for teams
Well-structured onboarding reduces time to productivity by 50% or more compared to informal approaches. New hires feel more confident in their roles, ask better questions, and integrate into team dynamics faster. Your existing team members spend less time answering basic questions because foundational information gets delivered systematically through the training program.
Effective onboarding transforms nervous new hires into confident contributors who understand both what to do and why it matters.
Examples and formats
Common formats include welcome videos from leadership, interactive policy acknowledgments, department-specific training modules, and buddy systems that pair new hires with experienced teammates. You might create a 30-day onboarding pathway that combines self-paced content with scheduled check-ins and hands-on projects.
How to measure results
Track completion rates for required modules, time to first productive output, 30/60/90-day retention rates, and new hire satisfaction scores. You can also measure manager feedback on how quickly new employees reach competency benchmarks compared to previous hires who went through different onboarding processes.
3. Compliance training
Compliance training ensures your employees understand and follow legal requirements, industry regulations, and internal policies that govern your business operations. This type of employee training protects your organization from legal liability, financial penalties, and reputational damage while creating a safer, more ethical workplace. You need documented proof that employees completed this training, which makes tracking and certification essential components.
What it covers
Your compliance program addresses regulatory requirements specific to your industry, such as HIPAA for healthcare, GDPR for data protection, or OSHA for workplace safety. It also covers anti-harassment policies, code of conduct, financial regulations, and environmental standards that apply to your operations. Most organizations combine general compliance topics with role-specific requirements based on employee responsibilities.
When to use it
You deploy compliance training during onboarding for all new hires and schedule recurring updates when regulations change or certifications expire. Many compliance topics require annual refresher courses to maintain valid certification status. You also launch targeted compliance training when your organization expands into new markets or introduces new processes that trigger additional regulatory requirements.
Benefits for teams
Proper compliance training reduces legal risk and creates clear behavioral standards across your organization. Employees gain confidence knowing they understand the rules, which decreases anxiety and improves decision-making in complex situations. Your organization avoids costly fines and maintains licenses needed to operate legally in your industry.
Compliance training transforms vague regulatory language into actionable guidelines that protect both your business and your people.
Examples and formats
Standard formats include mandatory online courses with knowledge checks, video scenarios, policy acknowledgment forms, and virtual instructor-led sessions for complex topics. You might deliver anti-harassment training through interactive scenarios, safety training through animated demonstrations, or data privacy training through branching simulations that test decision-making skills.
How to measure results
Track completion rates, assessment scores, certification status, and acknowledgment signatures through your LMS reporting dashboard. Monitor incident reports, audit findings, and regulatory inspection results to measure whether training translates into compliant behavior. You can also track time to completion for mandatory courses and identify employees who need additional support.
4. Technical skills training
Technical skills training teaches employees specific job-related competencies they need to perform their roles effectively. This type of employee training focuses on hands-on capabilities, software proficiency, equipment operation, or technical processes that directly impact work quality and efficiency. Unlike soft skills development, technical training delivers measurable, role-specific knowledge that employees apply immediately in their daily tasks.
What it covers
Your technical training program addresses software applications, programming languages, machinery operation, data analysis tools, and industry-specific systems your team uses regularly. It also includes troubleshooting procedures, quality control methods, and safety protocols for technical operations. Content depth ranges from basic user training to advanced certifications based on role complexity.
When to use it
Deploy technical skills training when you introduce new tools or systems, upgrade existing technology, or identify performance gaps in technical execution. You also need this training when employees transition to roles requiring different technical capabilities or when industry standards evolve and demand updated skills.
Benefits for teams
Proper technical training reduces errors, increases work speed, and improves output quality across your operations. Employees gain confidence using complex systems, which decreases frustration and support tickets for your IT team. Your organization maximizes technology investments by ensuring people actually know how to use the tools you purchase.
Technical training transforms expensive software and equipment into productivity multipliers that deliver measurable returns.
Examples and formats
Common approaches include hands-on workshops, video tutorials, interactive simulations, and certification programs from technology vendors. You might deliver Excel training through guided exercises, coding bootcamps through project-based learning, or equipment operation through supervised practice sessions.
How to measure results
Track certification completion rates, error reduction percentages, task completion times, and proficiency assessment scores. Monitor support requests and productivity metrics before and after training to quantify skill improvements.
5. Product and process training
Product and process training equips employees with detailed knowledge about your offerings and operational workflows. This type of employee training ensures teams understand how your products work, why customers buy them, and how to execute critical business processes consistently. You use this training to maintain quality standards, reduce mistakes, and help employees deliver accurate information to customers or execute internal procedures correctly.

What it covers
Your product training addresses features, benefits, use cases, technical specifications, and competitive advantages of everything you sell or support. Process training covers standard operating procedures, workflow steps, quality checkpoints, and troubleshooting methods for recurring business operations. Both types include real-world scenarios and decision trees that help employees handle variations they encounter on the job.
When to use it
Deploy this training when you launch new products, update existing offerings, or identify inconsistencies in how teams execute important processes. You also need it when employees transfer between departments, take on customer-facing roles, or when audit findings reveal process gaps that create quality or compliance issues.
Benefits for teams
Teams deliver consistent customer experiences and make fewer operational errors when everyone follows the same procedures. Employees answer product questions confidently, which increases customer trust and reduces escalations to senior staff. Your organization maintains quality standards and speeds up onboarding for complex roles.
Product and process training transforms fragmented knowledge into systematic expertise that scales across your entire workforce.
Examples and formats
Common formats include product demos, process flowcharts, interactive simulations, and job aids employees reference during actual work. You might create product training through guided walkthroughs or process training through step-by-step videos with knowledge checks.
How to measure results
Track certification completion rates, process adherence scores, error reduction percentages, and customer satisfaction metrics. Monitor how quickly employees answer product questions and whether they follow documented procedures consistently.
6. Sales enablement training
Sales enablement training provides your revenue teams with product knowledge, selling techniques, and customer engagement strategies they need to close deals effectively. This type of employee training bridges the gap between marketing materials and actual sales conversations by equipping your team with messaging frameworks, objection handling scripts, and competitive positioning that resonates with buyers. You deliver this training to accelerate ramp time for new sales reps and keep veteran sellers sharp on evolving products and market conditions.
What it covers
Your sales enablement program includes product features and benefits, ideal customer profiles, sales methodologies, and competitive differentiators your team references during prospect interactions. It also covers discovery question frameworks, objection responses, pricing strategies, and closing techniques that move deals through your pipeline. Most programs blend product education with behavioral coaching to build both knowledge and selling confidence.
When to use it
Deploy sales enablement training when you launch new products, enter new markets, or identify inconsistent messaging across your sales organization. You also need this training when sales cycles lengthen, win rates decline, or competitive threats increase. Many organizations schedule quarterly refreshers to reinforce best practices and update teams on product changes.
Benefits for teams
Proper sales training shortens ramp time for new hires by 30-50% and increases win rates by equipping everyone with proven approaches. Your team handles objections confidently, which reduces deal stalls and improves forecast accuracy. Representatives deliver consistent value propositions that strengthen your brand perception in the market.
Sales enablement training transforms product features into customer benefits that drive purchasing decisions.
Examples and formats
Common formats include role-playing exercises, recorded call reviews, competitive battle cards, and product demo walkthroughs. You might deliver objection handling through interactive scenarios or competitive training through comparison worksheets that sales reps reference during live calls.
How to measure results
Track quota attainment rates, average deal size, win/loss ratios, and sales cycle length before and after training interventions. Monitor certification completion, call quality scores, and discovery effectiveness to identify coaching opportunities.
7. Customer service training
Customer service training develops the communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and product knowledge your support teams need to handle customer interactions effectively. This type of employee training ensures representatives respond to inquiries consistently, resolve issues efficiently, and create positive experiences that build customer loyalty. You deliver this training to maintain service quality standards across all customer touchpoints, whether your team handles calls, emails, chat messages, or in-person interactions.
What it covers
Your customer service program includes active listening techniques, empathy building, conflict de-escalation, and clear communication strategies that help representatives understand and address customer needs. It also covers product troubleshooting, company policies, refund procedures, and escalation protocols your team references during support interactions. Most programs teach representatives how to balance efficiency with personalization to resolve issues quickly without making customers feel rushed.
When to use it
Deploy customer service training when you hire new support representatives, introduce new products or policies, or identify patterns in negative feedback. You also need this training when customer satisfaction scores decline or when you expand support channels that require different communication approaches.
Benefits for teams
Proper training reduces average handling time, increases first-contact resolution rates, and improves customer satisfaction scores across your support organization. Representatives handle difficult situations with confidence, which decreases stress and improves job satisfaction on your team. Your organization retains more customers and generates positive reviews that attract new business.
Customer service training transforms reactive problem-solving into proactive relationship-building that drives long-term loyalty.
Examples and formats
Common formats include call simulation exercises, email response templates, chat handling workshops, and recorded interaction reviews. You might deliver de-escalation training through role-playing scenarios or product knowledge through interactive troubleshooting guides.
How to measure results
Track customer satisfaction scores, first-contact resolution rates, average handling time, and escalation frequency before and after training interventions. Monitor quality assurance scores and customer feedback themes to identify ongoing coaching opportunities.
8. Leadership and manager training
Leadership and manager training develops the supervisory skills, strategic thinking, and people management capabilities your organization needs from individuals who guide teams. This type of employee training transforms strong individual contributors into effective leaders who drive team performance, develop talent, and execute business strategy. You invest in this training to reduce turnover caused by poor management, improve team productivity, and build a pipeline of capable leaders who can scale your operations.

What it covers
Your leadership program addresses coaching techniques, performance management, conflict resolution, and decision-making frameworks that separate good managers from great ones. It also includes delegation strategies, feedback delivery methods, goal setting, and change management skills that help leaders navigate complex organizational challenges. Most programs balance tactical management skills with strategic thinking to prepare leaders for current responsibilities and future growth.
When to use it
Deploy leadership training when you promote individual contributors into management roles, identify performance issues across teams, or prepare high-potential employees for advancement. You also need this training when employee engagement scores decline or when managers struggle with difficult conversations about performance or behavior.
Benefits for teams
Trained leaders increase employee retention by 25-40% and improve team productivity through better delegation and coaching. Your managers handle personnel issues confidently, which reduces HR escalations and creates more consistent employee experiences. The organization builds a stronger leadership bench that supports sustainable growth.
Leadership training multiplies your impact by equipping managers with skills that elevate entire teams rather than individual contributors.
Examples and formats
Common formats include cohort-based programs, executive coaching sessions, leadership assessments, and peer learning groups. You might deliver conflict resolution through facilitated practice sessions or strategic thinking through business simulation exercises.
How to measure results
Track employee engagement scores, team retention rates, promotion readiness assessments, and 360-degree feedback results for trained managers. Monitor goal achievement rates and employee satisfaction with management to measure leadership effectiveness improvements.
9. Communication and teamwork training
Communication and teamwork training builds the collaborative skills and interpersonal abilities your employees need to work effectively together. This type of employee training focuses on active listening, clear expression, constructive feedback, and conflict resolution that strengthens working relationships across departments and teams. You deliver this training to break down silos, improve project outcomes, and create a culture where employees collaborate naturally rather than working in isolation.
What it covers
Your communication program addresses verbal and written communication techniques, meeting facilitation, presentation skills, and cross-functional collaboration strategies that improve information flow. It also includes feedback frameworks, difficult conversation approaches, and team dynamics that help employees navigate interpersonal challenges productively. Most programs teach both individual communication skills and team collaboration methods.
When to use it
Deploy this training when you identify miscommunication patterns, form new project teams, or merge departments that need to work together. You also need it when employee surveys reveal collaboration issues or when remote work creates communication barriers that impact productivity.
Benefits for teams
Effective training reduces project delays caused by miscommunication and increases cross-functional collaboration by 30% or more. Your teams resolve conflicts faster, which decreases tension and improves workplace satisfaction. Projects finish on schedule because everyone understands expectations and communicates changes proactively.
Communication training transforms isolated workers into cohesive teams that solve problems collectively rather than individually.
Examples and formats
Common formats include team-building exercises, communication style assessments, facilitated workshops, and peer feedback sessions. You might deliver active listening through practice scenarios or collaboration through group problem-solving challenges.
How to measure results
Track project completion rates, meeting effectiveness scores, employee engagement metrics, and cross-departmental collaboration frequency before and after training. Monitor conflict resolution time and feedback quality to assess communication improvements.
10. Diversity and inclusion training
Diversity and inclusion training educates employees about unconscious bias, cultural differences, and inclusive workplace practices that create belonging for everyone on your team. This type of employee training addresses systemic barriers, microaggressions, and equity gaps that impact employee experience and business performance. You implement this training to build psychological safety, reduce discrimination, and leverage diverse perspectives that drive innovation and better decision-making across your organization.
What it covers
Your diversity program addresses unconscious bias recognition, cultural competency, inclusive language, and allyship behaviors that shape workplace interactions. It also includes accessibility requirements, religious accommodations, gender identity awareness, and generational differences that influence team dynamics. Most programs combine awareness building with actionable strategies employees use to create more inclusive environments.
When to use it
Deploy diversity training when you onboard new employees, identify bias patterns in hiring or promotion decisions, or expand into new markets with different cultural norms. You also need this training when employee resource groups request support or when engagement surveys reveal inclusion gaps affecting specific demographics.
Benefits for teams
Effective training reduces turnover among underrepresented groups by 20-30% and increases innovation by creating environments where diverse perspectives surface freely. Your teams make better decisions through inclusive problem-solving that considers multiple viewpoints. The organization attracts top talent from wider candidate pools and strengthens employer brand perception.
Diversity training transforms tolerance into active inclusion that unlocks the full potential of every employee.
Examples and formats
Common formats include facilitated workshops, scenario-based discussions, personal story sharing, and bias interruption practice sessions. You might deliver unconscious bias training through interactive assessments or inclusive leadership through small group conversations.
How to measure results
Track demographic representation in leadership roles, employee engagement scores by identity group, retention rates across demographics, and inclusion index scores from regular surveys. Monitor promotion rates and participation in development programs to identify remaining equity gaps.
11. Cybersecurity and data privacy training
Cybersecurity and data privacy training protects your organization from digital threats, data breaches, and privacy violations that can cost millions in damages and regulatory fines. This type of employee training teaches workers to recognize phishing attempts, handle sensitive information properly, and follow security protocols that safeguard company and customer data. You need this training because employees represent both your strongest defense and your weakest link in cybersecurity, depending on how well you prepare them to spot and respond to threats.
What it covers
Your cybersecurity program addresses password management, phishing recognition, social engineering tactics, and secure data handling practices that prevent unauthorized access. It also covers device security, remote work protocols, incident reporting procedures, and privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA that govern data collection and storage. Most programs include real-world attack examples that demonstrate how breaches happen.
When to use it
Deploy this training during employee onboarding, after security incidents, or when you introduce new systems that handle sensitive data. You also need annual refreshers because threat tactics evolve constantly and employees forget protocols over time.
Benefits for teams
Trained employees reduce successful phishing attacks by 70% or more and report suspicious activity faster, which limits breach impact. Your organization avoids costly data breaches, maintains customer trust, and stays compliant with privacy regulations.
Cybersecurity training transforms employees from security vulnerabilities into active defenders who protect your most valuable assets.
Examples and formats
Common formats include simulated phishing exercises, interactive threat scenarios, policy acknowledgment modules, and security awareness videos. You might deliver password training through guided tutorials or breach response through tabletop exercises.
How to measure results
Track phishing simulation click rates, security incident frequency, policy compliance rates, and time to incident reporting. Monitor audit findings and penetration test results to assess whether training translates into secure behaviors.
Next steps
You now understand the 11 core types of employee training that drive performance across modern organizations. Each type serves specific needs, from compliance requirements to leadership development, and choosing the right mix depends on your team’s skill gaps, business goals, and operational challenges. The most successful training programs combine multiple approaches through a centralized LMS platform that tracks progress, automates delivery, and proves ROI through detailed reporting.
Your next decision centers on implementation. You need to determine whether your current systems can support comprehensive training delivery or whether you need a dedicated platform that scales with your organization. Take our LMS readiness quiz to assess where you stand and identify the gaps between your current capabilities and what effective training actually requires. The quiz takes five minutes and provides personalized recommendations based on your specific situation, helping you build a training program that delivers measurable results rather than checking boxes.
