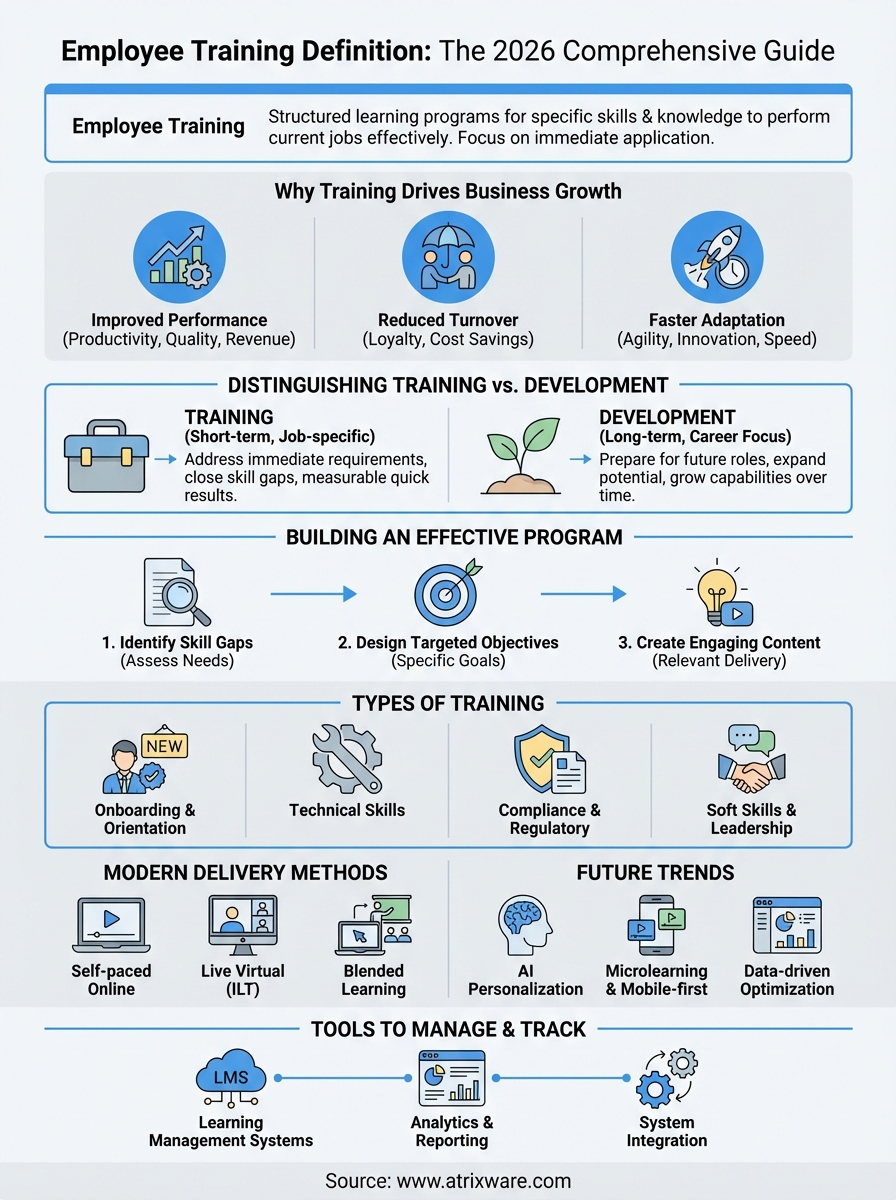
Employee training definition refers to structured learning programs that teach workers specific skills, knowledge, and competencies they need to perform their jobs effectively. Think of it as the intentional process where organizations equip their people with practical abilities that directly impact daily work performance. Training addresses immediate job requirements, whether that’s mastering new software, understanding safety protocols, or learning customer service techniques. The focus stays on building capabilities that employees can apply right away to do their current roles better.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about employee training. You’ll discover why training drives business growth, how it differs from employee development, and what makes a training program actually work. We’ll explore the various types of training you can implement, modern delivery methods that fit your workforce, and emerging trends reshaping how organizations approach learning. You’ll also get practical insights into the tools that help you manage and track training effectiveness. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for creating training programs that move your workforce forward.
Why employee training is vital for business growth
Your business grows when your people perform better, stay longer, and adapt faster to change. Training creates measurable improvements across all three areas, which directly translates to stronger financial performance. Organizations that invest consistently in employee training see higher productivity, lower turnover rates, and better customer satisfaction scores. The employee training definition we covered earlier points to skill building, but the business impact goes far beyond individual competence. When you train your workforce effectively, you’re building the foundation for sustainable growth that compounds over time.
Improved employee performance drives revenue
Training programs increase worker productivity by giving your team the exact skills they need to do their jobs efficiently. When employees know how to use tools correctly, follow best practices, and solve problems independently, they complete tasks faster and with fewer errors. A sales team trained in consultative selling techniques closes more deals. Customer service representatives trained in conflict resolution handle issues without escalation. Production workers trained on equipment safety reduce costly accidents and downtime.
The performance gains show up in your bottom line numbers. Studies consistently demonstrate that companies with comprehensive training programs generate higher revenue per employee than those without. You’ll also see improvements in quality metrics, customer retention rates, and operational efficiency. These aren’t abstract benefits; they’re concrete outcomes you can track and measure.
Reduced turnover saves hiring costs
Employees stay longer when you invest in their growth. Training signals that you value your people and want them to succeed, which builds loyalty and engagement. Workers who receive regular training opportunities feel more confident in their roles and see a clear path forward within your organization.
When you reduce turnover, you protect the knowledge and relationships your employees have built while eliminating the massive costs of replacement.
Consider the full expense of losing an employee. You’ll spend money on recruitment advertising, interviewer time, background checks, and onboarding new hires. The real cost includes lost productivity during the vacancy period and the months it takes for replacements to reach full performance. Industry estimates put replacement costs at 50% to 200% of an employee’s annual salary, depending on the role. Training programs that improve retention by even a small percentage deliver substantial savings.
Faster adaptation to market changes
Your business needs agility to compete in rapidly evolving markets. Training creates a workforce that can quickly learn new technologies, adjust to process changes, and embrace innovation. When your industry shifts, trained employees adapt without the long learning curves that slow down unprepared organizations.
Technology adoption provides a clear example. Companies that train workers on new software platforms deploy those systems faster and extract value sooner than competitors who skip training. Your trained employees also identify opportunities to apply new tools in creative ways that improve workflows and customer experiences. This adaptability becomes a competitive advantage that separates market leaders from followers.
Training also prepares your organization for strategic pivots. Whether you’re entering new markets, launching products, or changing business models, a well-trained workforce can execute your strategy effectively. You won’t waste months bringing people up to speed because they already have the learning capabilities and foundational knowledge to absorb new information quickly. This speed advantage lets you capture opportunities while competitors are still planning.
How to distinguish training from development
Many organizations confuse employee training with employee development, but these two concepts serve different purposes in your talent strategy. Understanding the distinction helps you allocate resources correctly and set appropriate expectations for each initiative. The employee training definition we established earlier focuses on immediate job performance, while development prepares employees for future roles and responsibilities. You’ll make better decisions about program design, budget allocation, and success metrics when you recognize these fundamental differences.

Focus on time horizons
Training addresses current job requirements with a short-term perspective. When you train employees, you’re helping them master the skills they need today to perform their existing duties effectively. A training program might teach your customer service team how to use your new ticketing system or show warehouse workers proper lifting techniques. You’ll see results within days or weeks as employees apply what they learned immediately.
Development takes a long-term view focused on preparing people for future positions. Your development initiatives build broad capabilities that employees will use later in their careers, often in roles they don’t hold yet. Leadership development programs, for example, cultivate strategic thinking and people management skills that individual contributors won’t use until they move into supervisory positions. You might invest years in developing high-potential employees before seeing the full return.
Different objectives and outcomes
Training programs aim to close specific skill gaps and improve current performance metrics. You’ll measure training success through productivity increases, error reduction, or faster task completion. The outcomes directly connect to job requirements and business operations you can quantify today.
Development programs build capabilities that support career progression and organizational adaptability over time.
Development initiatives focus on expanding potential rather than fixing immediate deficiencies. You’re investing in competencies like critical thinking, innovation, or cross-functional collaboration that prepare employees for broader responsibilities. Development outcomes appear gradually as people take on new challenges and advance through your organization.
Measurement approaches
You measure training effectiveness through performance improvements tied to specific skills. Did sales conversion rates increase after negotiation training? Did safety incidents decline after equipment training? These concrete metrics show whether training achieved its intended impact quickly.
Development requires different measurement methods focused on readiness and potential. You’ll track career progression rates, succession pipeline strength, and employee engagement scores rather than immediate performance changes. The assessment timeline extends months or years instead of weeks because development impacts manifest slowly as employees grow into expanded roles.
How to build an effective employee training program
Building an effective training program requires a systematic approach that connects learning activities to business outcomes. You can’t simply throw content at employees and hope for improvement. The employee training definition we established earlier emphasizes structured learning for job performance, and that structure starts with intentional program design. Your training program needs clear objectives, relevant content, and measurable results that justify your investment. When you follow a proven framework, you’ll create programs that employees actually complete and apply in their daily work.
Identify specific skill gaps and business needs
Start by conducting a thorough skills assessment to understand what your workforce can and cannot do effectively. You’ll gather this information through performance reviews, manager feedback, customer complaints, and direct observation of work processes. Look for patterns where employees struggle consistently or where quality issues emerge repeatedly.
Connect these skill gaps to specific business priorities rather than creating training for its own sake. If you’re losing customers due to poor service interactions, your training needs focus on communication and problem-solving skills. When production errors cost money, your priority becomes technical competency and quality control. This alignment ensures your training program addresses real problems that impact your bottom line.
Design targeted learning objectives
Write specific, measurable objectives that define what employees should accomplish after completing training. Avoid vague goals like "understand customer service" and instead specify "resolve customer complaints in one interaction 80% of the time." Your objectives should describe observable behaviors and performance standards you can verify.
Your learning objectives drive everything else in your training program, from content selection to assessment methods.
Break complex skills into smaller components that employees can master progressively. Teaching project management might start with task prioritization, then advance to resource allocation, and finally cover stakeholder communication. This sequencing helps learners build confidence and competence systematically rather than overwhelming them with too much information at once.
Create engaging content and delivery methods
Develop training materials that match how your employees learn best and fit their work schedules. Busy frontline workers might need short video modules they can watch on mobile devices, while office staff might benefit from interactive workshops. Consider using real scenarios from your workplace rather than generic examples that don’t resonate.
Mix different content formats to maintain engagement and retention. Combine demonstrations, practice exercises, case studies, and knowledge checks throughout your program. You’ll also want to provide job aids and reference materials that employees can access after training when they need support applying new skills.
Types of training programs to implement
Your organization needs different training programs to address varied learning needs across your workforce. The employee training definition we established earlier covers skill building for job performance, but those skills fall into distinct categories that require different approaches. You’ll maximize your training investment by implementing a balanced portfolio of programs rather than focusing on just one type. Each training category serves specific business purposes and delivers unique outcomes that support your overall talent strategy.
Onboarding and orientation programs
Onboarding training brings new hires up to speed quickly on your company culture, policies, and job-specific responsibilities. You’ll cover essential information like workplace safety, organizational structure, benefits enrollment, and performance expectations during this critical period. Effective onboarding programs reduce time to productivity and help new employees feel connected to your organization from day one.

Your onboarding should extend beyond the first week to include role-specific training that builds job competence over the first 90 days. This might involve shadowing experienced workers, completing certification requirements, or mastering your core systems and processes. Companies with structured onboarding programs see higher retention rates and faster performance ramps than those using informal approaches.
Skills-based technical training
Technical training develops the specialized knowledge employees need to operate equipment, use software, or perform job-specific tasks correctly. You’ll provide this training when introducing new technologies, updating processes, or helping employees master complex procedures that require precision. Manufacturing workers might receive training on machinery operation, while office employees learn your CRM platform or data analysis tools.
Technical training delivers immediate productivity gains because employees apply these skills directly in their daily work.
This training type often requires hands-on practice and repeated application before employees achieve proficiency. You’ll need to schedule ongoing refresher sessions to maintain skill levels and update knowledge as your tools and processes evolve.
Compliance and regulatory training
Compliance training ensures your workforce understands and follows legal requirements and industry regulations that govern your business operations. You’ll implement this training to avoid penalties, protect employee safety, and maintain certifications necessary for operating in your industry. Common topics include harassment prevention, data privacy, workplace safety, and industry-specific regulations like HIPAA for healthcare or SOX for public companies.
Your compliance training needs regular updates to reflect changing regulations and must include documentation proving employees completed required courses. Many organizations schedule annual refreshers to keep compliance knowledge current across their entire workforce.
Soft skills and leadership training
Soft skills training builds interpersonal capabilities like communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence that improve workplace relationships and collaboration. You’ll invest in these programs to enhance customer interactions, reduce workplace conflicts, and prepare employees for leadership responsibilities. This training becomes particularly valuable as employees advance in their careers and take on roles requiring people management and strategic thinking.
Modern methods for delivering training
Your training delivery method determines how effectively employees absorb and apply new skills. The employee training definition centers on structured learning, and modern technology has transformed how you deliver that structure to your workforce. You now have multiple options beyond traditional classroom instruction that offer greater flexibility and cost efficiency. Choosing the right delivery method depends on your content type, employee preferences, budget constraints, and business needs.
Self-paced online learning platforms
Online learning platforms let employees complete training on their own schedule without instructor coordination or physical classroom space. You’ll provide access to video modules, interactive simulations, and knowledge assessments that workers progress through at their own pace. This method works particularly well for technical skills training where employees need to review complex procedures multiple times or for compliance courses that everyone must complete annually.
Self-paced training reduces costs by eliminating travel expenses, venue rentals, and instructor fees while allowing employees to learn during downtime periods that fit their workflow. Your workers can pause, rewind, and revisit content as needed, which improves retention for complex topics. However, you’ll need strong accountability measures like completion tracking and manager follow-up to ensure employees actually finish courses without instructor pressure.
Live virtual instructor-led training
Virtual classrooms combine the personal interaction of traditional training with the convenience of remote access. You’ll use video conferencing platforms to deliver real-time instruction where employees can ask questions, participate in discussions, and complete group activities from their desks or home offices. This method suits soft skills training like leadership development or customer service where discussion and feedback drive learning.
Virtual instructor-led training eliminates travel costs while maintaining the engagement and accountability that live instruction provides.
Your trainers can read participant reactions, adjust pacing based on comprehension, and provide immediate clarification when concepts confuse learners. You’ll also record sessions for employees who miss the live event or need to review material later.
Blended learning approaches
Blended programs combine multiple delivery methods to maximize learning effectiveness and operational efficiency. You might assign online modules for foundational knowledge, then bring employees together for hands-on practice and application workshops. This approach lets workers absorb basic concepts independently before using valuable instructor time for complex skill development and problem-solving exercises.
Manufacturing companies often use blended training by having employees watch safety videos online before practicing procedures with equipment on the factory floor. Sales organizations assign product knowledge courses online, then conduct live role-playing sessions for pitch refinement.
Key trends shaping the future of training
The way organizations approach employee training continues to evolve rapidly as new technologies emerge and workforce expectations shift. You’ll see these trends transforming how companies design, deliver, and measure learning programs over the next several years. Understanding these changes helps you stay competitive in attracting and developing talent while maximizing your training investment returns. The employee training definition itself expands as these innovations create new possibilities for how people acquire skills and knowledge in workplace settings.

Artificial intelligence personalizing learning experiences
AI-powered systems now adapt training content to match individual learning styles, skill levels, and career goals automatically. You can deploy platforms that analyze how each employee interacts with training materials and then adjust difficulty, pacing, and content formats accordingly. Workers who grasp concepts quickly move through material faster, while those needing extra support receive additional practice and alternative explanations without instructor intervention.
These intelligent systems also recommend relevant courses based on employee performance gaps, career aspirations, and emerging skill requirements in your industry.
Your training programs become more efficient because employees spend time only on content they actually need rather than sitting through material they’ve already mastered. AI also enables chatbot assistants that answer employee questions during training and provide just-in-time support when workers apply new skills on the job.
Microlearning and mobile-first delivery
Short training modules designed for mobile consumption now replace lengthy courses that require dedicated computer time. You’ll create three to five-minute lessons employees can complete during work breaks, commutes, or downtime between tasks. This approach recognizes that modern workers struggle to find extended blocks of uninterrupted time for traditional training sessions.
Mobile-first design ensures your training materials display correctly on smartphones and tablets rather than requiring desktop access. Employees complete courses wherever they are, which increases completion rates dramatically compared to desktop-only programs. Your workforce also retains information better when learning happens in small, focused increments rather than marathon sessions.
Data-driven training optimization
Advanced analytics platforms track detailed metrics beyond simple completion rates to measure actual skill development and business impact. You’ll monitor which training content drives performance improvements, where employees struggle most, and what learning paths produce the fastest competency growth. This data helps you continuously refine programs by eliminating ineffective content and doubling down on what works.
Predictive analytics also identify employees at risk of underperformance before problems become serious, allowing you to intervene with targeted training. You can measure training ROI with precision by connecting learning activities directly to productivity gains, quality improvements, and retention outcomes.
Tools to manage and track employee training
Your organization needs specialized software to organize training programs, track employee progress, and measure learning outcomes effectively. You can’t rely on spreadsheets and manual processes when managing training across dozens or hundreds of employees. The right tools automate administrative tasks, centralize training records, and provide visibility into who needs which skills. Modern training management platforms have evolved far beyond simple course catalogs to become strategic systems that connect learning activities directly to business performance metrics.
Learning management systems (LMS)
A learning management system serves as your central hub for delivering courses, tracking completions, and storing training records in one accessible location. You’ll use an LMS to upload training content, assign courses to employees, send automatic reminders, and generate compliance reports without manual intervention. These platforms support various content types including videos, documents, quizzes, and interactive simulations that employees access through web browsers or mobile apps.
Your LMS should simplify both the learner experience and administrator workflows rather than creating complexity. Employees need intuitive interfaces where they can quickly find assigned training, track their progress, and access reference materials after course completion. Administrators require drag-and-drop builders for creating courses rapidly plus customizable reporting tools that answer specific questions about training effectiveness and compliance status.
Modern LMS platforms also manage automated workflows that notify managers when employees complete training or fall behind schedule, reducing your administrative burden significantly.
Training analytics and reporting dashboards
Analytics tools transform raw training data into actionable insights about program effectiveness and skill development across your workforce. You’ll monitor completion rates, assessment scores, time-to-proficiency metrics, and correlations between training activities and performance improvements. These dashboards help you identify which courses deliver results and which need revision or elimination from your catalog.
Your analytics should also track certification expirations and upcoming compliance deadlines so you can schedule refresher training proactively. This visibility prevents gaps that create regulatory risks or allow critical skills to deteriorate over time.
Integration capabilities with existing systems
Training tools that connect with your HR systems, payroll platforms, and performance management software create seamless workflows that reduce duplicate data entry. You’ll sync employee records automatically so new hires appear in your training system immediately while terminations close access without manual updates. Integration with performance review systems lets you tie skill gaps identified during evaluations directly to training assignments that address those deficiencies.
These connections also enable you to measure training ROI by linking learning activities to outcomes tracked in other systems like sales performance, customer satisfaction scores, or quality metrics. The employee training definition emphasizes structured learning for job performance, and integrated systems help you verify that learning actually improves the specific performance indicators that matter to your business.
Moving your workforce forward
Understanding the employee training definition we explored throughout this guide gives you a foundation for creating programs that deliver measurable business results. You’ve learned how training drives growth through improved performance, reduced turnover, and faster adaptation to market changes. The distinction between training and development helps you allocate resources correctly, while modern delivery methods make learning more accessible and effective. Building programs with clear objectives, engaging content, and comprehensive tracking ensures your investment produces actual skill development rather than wasted time.
Your next step involves assessing where your organization stands today and identifying the systems you need to scale training effectively. Taking a systematic approach to evaluating your requirements helps you avoid costly mistakes and select solutions that match your specific needs. Discover your LMS readiness level to understand which capabilities matter most for your training goals and determine what stage you’re at in building a comprehensive learning program that moves your entire workforce forward.
