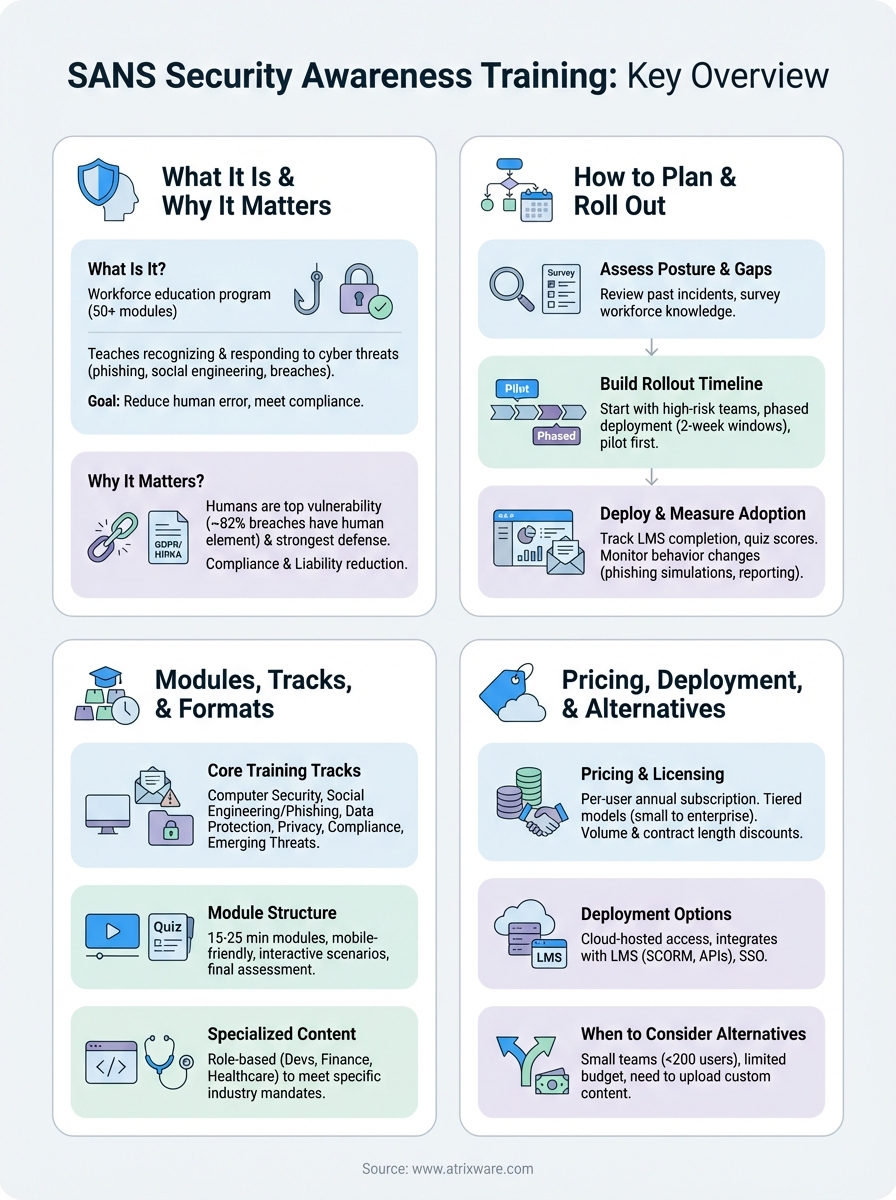
SANS Security Awareness Training is a workforce education program that teaches your employees how to recognize and respond to cyber threats like phishing attacks, social engineering, and data breaches. Created by SANS Institute, the program delivers expert developed content through 50+ training modules organized into tracks covering everything from basic security hygiene to advanced compliance requirements. Organizations use it to reduce human error, meet regulatory standards, and build a security conscious culture across their teams.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know about implementing SANS training. You’ll learn why companies choose SANS over other security awareness platforms, how to plan and execute a successful rollout, what modules and tracks are available, and how pricing and licensing actually work. We’ll also help you figure out whether SANS fits your existing training infrastructure or if you should consider alternatives that better match your budget and technical requirements.
Why SANS security awareness training matters
Your employees are your biggest security vulnerability and your strongest defense line at the same time. About 82% of data breaches involve a human element, whether that’s clicking a phishing link, using weak passwords, or falling for social engineering tactics. SANS security awareness training directly addresses this gap by turning your workforce into an active security layer rather than a passive risk factor that threat actors can exploit.

The human element drives most breaches
Security technology alone can’t protect your organization when an employee unwittingly grants access to a threat actor. Your firewall and antivirus software become irrelevant the moment someone enters their credentials on a fake login page or opens a malicious attachment. Training gives your team the pattern recognition skills they need to spot suspicious emails, unusual requests, and compromised links before damage occurs.
Traditional security tools stop automated attacks, but only trained employees can defend against targeted social engineering.
Most attacks succeed not because of technical vulnerabilities but because someone made a split second decision without recognizing the warning signs. SANS modules teach people to pause, verify, and report instead of clicking reflexively.
Compliance and liability reduction
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require documented security training for employees who handle sensitive data. Without a formal program, you face audit failures, penalties, and potential legal liability when breaches occur. SANS provides audit ready documentation that proves your organization met its due diligence requirements. Insurance companies also increasingly require security awareness training as a condition for cyber liability coverage, making it a practical business necessity beyond just compliance checkboxes.
How to plan and roll out SANS training
Rolling out SANS security awareness training requires more than just buying licenses and sending login credentials to your team. You need a structured deployment plan that accounts for your organization’s specific risks, existing security culture, and operational constraints. A successful implementation starts with assessment, moves through phased deployment, and ends with ongoing measurement that proves your investment delivers real behavior change.
Assess your current security posture and gaps
Start by identifying which security incidents have affected your organization in the past 12 months. Review help desk tickets, IT security logs, and any breach reports to find patterns in how employees interact with threats. If phishing attempts consistently bypass your email filters, or if people regularly share passwords, those vulnerability areas should drive your module selection and training priorities.

Survey your workforce to understand their baseline security knowledge and attitudes. Anonymous questionnaires reveal whether employees know how to verify suspicious links, understand data classification policies, or feel comfortable reporting potential security incidents. This baseline data helps you measure improvement after training launches and shows executives the tangible impact of your program investment.
Build your rollout timeline
Deploy training in phases rather than company wide all at once. Start with departments that handle the most sensitive data or face the highest threat exposure, like finance teams who process wire transfers or customer service representatives who verify account information. This approach lets you refine your messaging and troubleshoot technical issues before expanding to the entire organization.
Pilot programs with high risk teams give you proof points to secure broader organizational buy in.
Set clear completion deadlines that align with your compliance requirements but allow enough flexibility for employees to fit training into their schedules. Most organizations see better engagement with two week completion windows rather than aggressive three day mandates that create resentment and rushed learning.
Deploy and measure adoption
Configure your learning management system to track completion rates, quiz scores, and time spent in each module. SANS provides detailed reporting, but you need to establish who reviews this data weekly and what intervention triggers matter for your organization. If completion rates drop below 70% at the one week mark, send reminder emails or have managers follow up directly with their teams.
Track real world security behavior changes alongside training metrics. Monitor phishing simulation results, password reset requests, and security incident reports to see whether training translates into actual behavior shifts. If people complete modules but still click simulated phishing emails at the same rate, you need to adjust your delivery method or increase reinforcement frequency rather than just celebrating completion statistics.
SANS modules, tracks, and formats
SANS security awareness training organizes its content library into 50+ individual modules grouped across six primary tracks that cover different security domains and risk areas. Each track targets specific threats and compliance requirements, letting you assign training based on job roles, department risk levels, and regulatory obligations. You can deploy modules as standalone units or combine them into learning paths that progress from basic security hygiene to advanced threat recognition.
Core training tracks and their focus areas
The Computer Security track covers foundational topics every employee needs, including password management, secure browsing habits, physical security, and mobile device protection. This track forms the baseline for most deployment strategies because it addresses the most common attack vectors that affect all staff regardless of technical skill level. You assign these modules to your entire workforce during onboarding and refresh them annually to reinforce core concepts.

Social Engineering and Phishing modules teach people to recognize manipulation tactics, verify requests before taking action, and report suspicious communications. These modules use real world examples of business email compromise, pretexting, and credential harvesting to show how attackers exploit trust and urgency. Most organizations pair this track with simulated phishing campaigns to measure whether training translates into changed behavior when employees face actual threats.
Additional tracks focus on Data Protection, Privacy, Compliance, and Emerging Threats. The Data Protection track covers classification policies, encryption, and secure file handling. Privacy modules address GDPR, CCPA, and other regional regulations. Compliance content maps to specific industry requirements like HIPAA for healthcare or PCI DSS for payment processing. The Emerging Threats track updates regularly to cover new attack methods, including AI powered social engineering and deepfake risks.
Individual module structure and delivery
Each module runs 15 to 25 minutes and includes video content, interactive scenarios, knowledge checks, and a final assessment. SANS designs modules for mobile delivery, desktop browsers, and learning management system integration, so employees can complete training on their preferred device. The platform tracks completion status, quiz scores, and time spent to generate compliance documentation your auditors will accept.
Short, focused modules fit into busy schedules better than hour-long training sessions that interrupt workflow.
You can customize module sequencing, set completion deadlines, and configure passing scores based on your organization’s requirements. Most companies require 80% quiz performance to pass, but you can adjust this threshold for departments that handle particularly sensitive data or face higher regulatory scrutiny.
Specialized compliance and role-based content
SANS offers specialized modules for specific job functions and vertical markets beyond the core tracks. Developers get secure coding modules that cover input validation, authentication, and common vulnerability patterns. Finance teams access wire fraud prevention and invoice verification content. Customer service representatives learn to authenticate callers and protect account information during support interactions.
Healthcare organizations can assign HIPAA specific modules that cover protected health information handling, breach notification requirements, and electronic medical record security. Financial services companies access content addressing SEC regulations, anti-money laundering requirements, and customer data protection standards. These specialized modules let you meet industry specific compliance mandates without building custom training content from scratch or hiring external consultants to develop role-based curricula.
Pricing, licensing, and deployment options
SANS structures its pricing around per-user annual subscriptions rather than one-time purchases or perpetual licenses. The company doesn’t publish standard rates publicly because costs vary based on your organization size, module selection, and contract length. You typically get quotes starting around $20 to $40 per user per year for basic packages, with enterprise deployments and specialized compliance modules pushing costs higher depending on your specific requirements and negotiated volume discounts.
Cost structure and licensing models
SANS offers tiered licensing that scales from small businesses to global enterprises. Small organizations with under 100 employees access starter packages that include core modules and basic reporting. Mid-market companies get expanded module libraries, custom branding options, and advanced analytics. Enterprise agreements add dedicated account management, custom content development, and integration support for complex technology stacks.

Your license determines which module tracks you can access and how many users can complete training simultaneously. Basic tiers typically include the Computer Security and Social Engineering tracks, while comprehensive packages unlock all six tracks plus specialized compliance content. You can add modules individually if you need specific training without upgrading your entire license tier, though this approach usually costs more per module than bundled packages.
Volume pricing drops your per-user cost significantly once you exceed 500 seats, making SANS more competitive for larger deployments.
Contract length affects your rates substantially. Annual agreements give you standard pricing, but multi-year commitments often secure 10% to 20% discounts. SANS also offers educational discounts for schools and nonprofits, though you need to verify eligibility and provide documentation during the quote process.
Deployment and implementation options
SANS delivers training through cloud-hosted access that requires no on-premises infrastructure or software installation. You integrate the platform with your existing learning management system through SCORM packages, REST APIs, or direct LMS connectors. This deployment model lets you launch sans security awareness training within days rather than weeks of procurement approval.
Organizations with strict data sovereignty requirements can request specific hosting regions, though this option typically appears only in enterprise contracts and may increase costs. You get SSL encryption, redundant backups, and compliance with major security frameworks including SOC 2 and ISO 27001 as standard features across all deployment tiers.
Implementation includes onboarding support where SANS specialists help you configure your portal, upload user data, and establish reporting workflows. Basic packages provide email and knowledge base support, while premium tiers add live chat, phone assistance, and quarterly business reviews. Your contract should specify response time guarantees and whether you get a dedicated customer success manager or share support resources across multiple accounts.
Fitting SANS into your stack or choosing alternatives
SANS security awareness training integrates with most corporate technology stacks through standard protocols and APIs, but you need to evaluate whether it aligns with your existing infrastructure, budget constraints, and specific training requirements. The platform works best for organizations with established LMS systems, dedicated security teams, and budgets that accommodate premium pricing. Smaller companies or those with simpler training needs might find better value in alternatives that offer comparable content at lower price points or with different licensing models.
Integration capabilities and technical requirements
Your existing learning management system determines how smoothly you can deploy SANS modules. The platform supports SCORM 1.2 and 2004 standards, xAPI (Tin Can), and AICC packages that work with most enterprise LMS platforms. You can also integrate user directories through SAML single sign-on, LDAP synchronization, or CSV imports that automate user provisioning and eliminate manual account management overhead.
Direct API access gives you flexibility to build custom workflows and reporting dashboards that match your security operations processes.
Organizations using Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace can leverage native SSO integrations that let employees access training without creating separate credentials. SANS also provides webhooks for real-time completion notifications, letting you trigger automated workflows in your security information and event management system or ticketing platform when employees finish critical modules.
When to consider alternative platforms
You should evaluate competing platforms if your organization has fewer than 200 employees and limited security awareness budgets. Many alternatives offer similar module libraries, phishing simulation tools, and compliance reporting at 30% to 50% lower costs than SANS enterprise pricing. These platforms typically sacrifice some content depth and customization options but deliver adequate protection for standard threat scenarios.
Companies with existing training content libraries might benefit from platforms that let you upload custom modules alongside vendor provided content. SANS focuses primarily on its proprietary curriculum, making it less flexible if you want to combine internal security policies with external training materials in a single learner experience.
Wrapping up
SANS security awareness training delivers expert-developed content and comprehensive compliance features that help organizations reduce human-driven security risks across their workforce. The platform works well for companies with established training infrastructure, dedicated security teams, and budgets that support premium pricing for specialized modules. Your decision to implement SANS or choose an alternative depends on your specific requirements, existing technology stack, and how much flexibility you need in customizing content delivery and integration capabilities.
If you’re evaluating learning management systems for security awareness or broader training needs, take our LMS readiness quiz to determine where you are in the purchase process and what features matter most for your organization.
