You bought an LMS. Now you need to get it running without blowing deadlines, burning through your budget, or confusing everyone on your team. The problem is that most implementations fail because organizations jump in without a clear plan. You end up with missed integrations, confused stakeholders, and training content that arrives three weeks late.
A solid implementation checklist keeps you organized. It maps out every task, assigns clear ownership, and gives you a timeline that actually works. You stop forgetting critical steps and start making measurable progress.
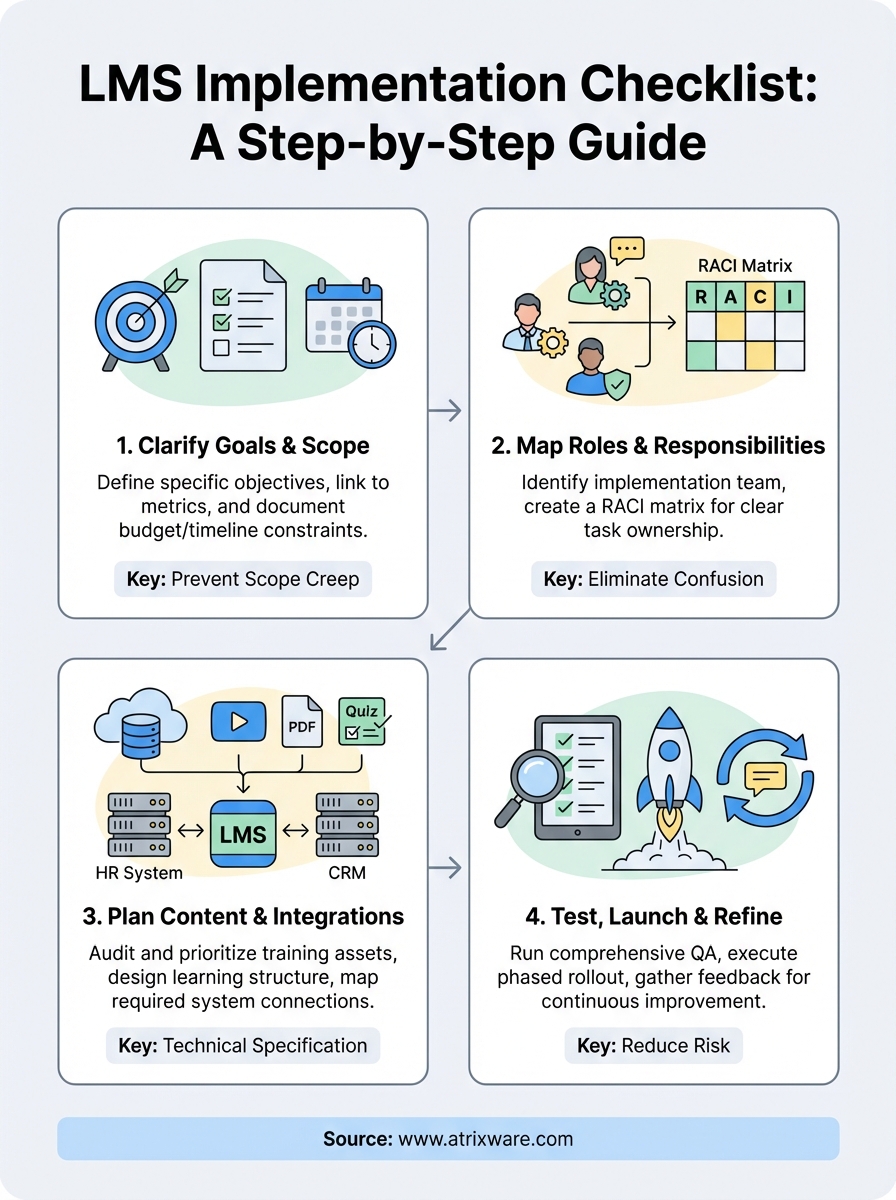
This guide walks you through building your own LMS implementation checklist from scratch. You’ll learn how to define your goals and constraints, map stakeholder responsibilities, plan your content and integrations, then test and launch your system. By the end, you’ll have a framework that turns a messy rollout into a manageable project.
Why you need an LMS implementation checklist
Your LMS implementation involves dozens of moving parts. You need to migrate user data, configure security settings, build training courses, integrate with your CRM and HR systems, train administrators, and coordinate across multiple departments. Without a structured plan, critical tasks fall through the cracks. Your launch date slips by three months, your IT team discovers integration conflicts in week five, and your content creators realize they don’t have platform access until the day before go-live.
An LMS implementation checklist gives you visibility and control over every task. You know exactly what needs to happen, who owns each deliverable, and when each milestone should hit. Your team stops duplicating work or waiting on dependencies that nobody tracked. Instead of reacting to surprises, you prevent problems before they start.
A checklist transforms your implementation from a chaotic scramble into a predictable project with measurable progress at every stage.
What your checklist prevents
The most common implementation failures come from poor planning and unclear ownership. Teams launch without testing integrations, content arrives incomplete, or key stakeholders don’t understand their responsibilities until it’s too late. A proper lms implementation checklist addresses these risks directly by documenting every requirement upfront. You catch gaps early, assign clear accountability, and build in time for testing before your users see the system.
Step 1. Clarify goals, scope, and constraints
Your lms implementation checklist starts with defining exactly what success looks like for your organization. You need specific, measurable objectives before you assign tasks or build timelines. Start by asking what business problem your LMS solves. Are you reducing compliance training costs by 30%? Cutting employee onboarding time from eight weeks to three? Generating $200K in annual revenue from customer training courses? Write down three to five concrete goals that your leadership team agrees on. These become your north star throughout the implementation.
Define your business objectives
You transform vague intentions into actionable targets by linking each goal to a metric you can track. If your goal is faster onboarding, measure time to productivity for new hires. If you want better compliance, track certification completion rates and audit failures. Document who owns each metric and how you’ll report progress.
Your objectives shape every decision downstream. A compliance-focused implementation requires audit trails and certification tracking, while a customer training program prioritizes e-commerce integration and branded portals. List your must-have features based on these objectives, then separate them from nice-to-have capabilities you can add later.
Clear objectives prevent scope creep by giving you an objective filter for every feature request that surfaces during implementation.
Document constraints and timelines
Realistic constraints keep your project grounded in what’s actually possible. You need to document your budget, including licensing costs, implementation services, content development, and ongoing support. Write down your hard launch date if you have one, along with any regulatory deadlines that can’t move. Identify resource limits like the number of administrators you can dedicate to setup or the subject matter experts available for content creation.
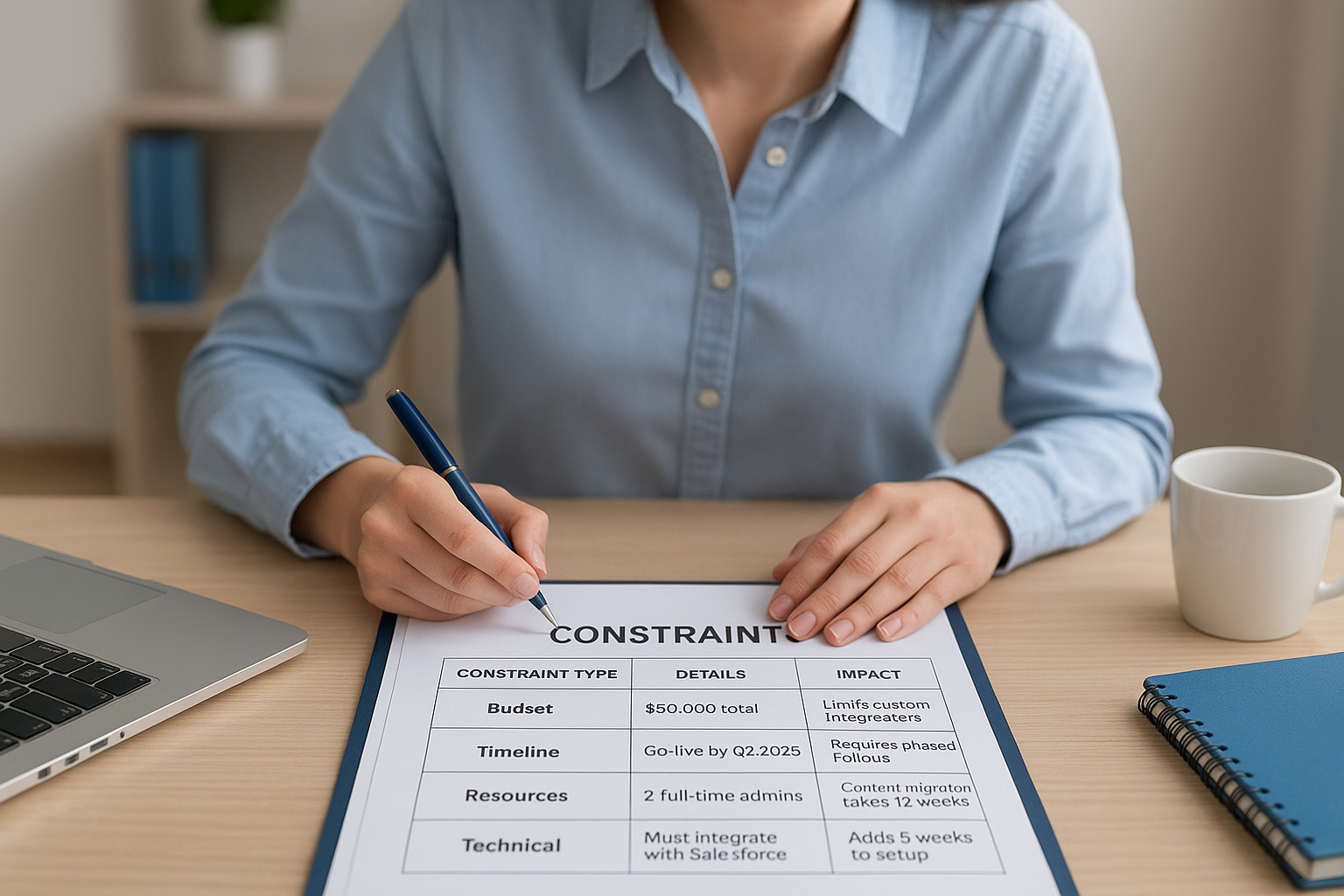

Create a simple constraints document:
| Constraint Type | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Budget | $50,000 total | Limits custom integrations |
| Timeline | Go-live by Q2 2026 | Requires phased rollout |
| Resources | 2 full-time admins | Content migration takes 12 weeks |
| Technical | Must integrate with Salesforce | Adds 3 weeks to setup |
This document becomes your reality check when stakeholders request additional features or accelerated timelines. You refer back to it whenever scope starts expanding beyond what your constraints allow.
Step 2. Map stakeholders, roles, and responsibilities
Your lms implementation checklist needs clear ownership for every task. Without explicit role assignments, tasks get ignored because everyone assumes someone else will handle them. You prevent this by mapping out who does what before the project starts. Your implementation team typically includes a project manager to drive progress, IT specialists for integrations and security, content creators or subject matter experts for course development, and department heads who represent end users.
Identify your implementation team
Start by listing every person who touches the project. You need someone from IT to configure system settings and manage integrations with your existing platforms. Your HR or training department provides subject matter expertise for course content and understands learner needs. Add a representative from finance if you plan to sell training or need budget approvals. Include at least one executive sponsor who can remove blockers and secure resources when you hit roadblocks.
Document why each person is on the team and what specific expertise they bring. This prevents overlap and ensures you have coverage for critical skills like technical configuration, content creation, and stakeholder communication.
Create a responsibility matrix
Build a simple RACI matrix that maps tasks to people. RACI stands for Responsible (does the work), Accountable (owns the outcome), Consulted (provides input), and Informed (receives updates). This format gives you instant clarity on who drives each deliverable.

| Task | Responsible | Accountable | Consulted | Informed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configure SSO | IT Lead | Project Manager | Security Team | All Admins |
| Migrate user data | IT Specialist | Data Manager | HR Director | Project Manager |
| Build compliance courses | Content Creator | Training Director | Legal Team | Executive Sponsor |
| Test integrations | QA Team | IT Lead | Project Manager | All Stakeholders |
A responsibility matrix eliminates confusion by showing exactly who owns each task and who needs to provide input along the way.
Your matrix becomes the single source of truth for accountability throughout the implementation.
Step 3. Plan content, structure, and integrations
Your lms implementation checklist enters its most technical phase when you start planning what goes inside the system and how it connects to your existing infrastructure. You need to decide whether you’ll migrate existing training materials, create new courses from scratch, or use a combination of both. Your content strategy directly affects your timeline and budget because building courses takes longer than migrating them. At the same time, you must map out how your LMS connects to systems like your HR platform, CRM, payment processor, and authentication service.
Build your content migration plan
You start by auditing every training asset you currently own. Document each course, video, PDF, quiz, and certification program. Note the format of each asset (SCORM, xAPI, PowerPoint, video) and its current location. Create a simple spreadsheet that tracks what content you’ll keep, what needs updating, and what you’ll retire.
Your migration plan should prioritize critical content first. Move compliance training and onboarding courses before nice-to-have professional development materials. This approach gets your most important programs live faster and reduces risk if your timeline compresses.
| Content Type | Current Format | Migration Priority | Estimated Hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance training | SCORM 1.2 | High | 20 hours |
| Product videos | MP4 | High | 8 hours |
| Leadership courses | PowerPoint | Medium | 40 hours |
| Sales playbooks | Low | 12 hours |
Prioritizing content by business impact ensures your LMS delivers value immediately rather than waiting until every course migrates.
Structure your learning hierarchy
You need to design how learners navigate your training content before you upload anything. Your structure might use learning paths that group related courses, categories that organize content by department or skill, or certifications that require specific course sequences. Map out this hierarchy on paper first to catch organizational problems early.
Your portal structure matters if you train multiple audiences like employees, customers, and partners. Each group needs its own branded experience with relevant content. Document which portals you need, what content lives in each one, and who administers them.
Map required integrations
List every system your LMS must connect to for it to work properly. Your HR system provides employee data for auto-enrollment. Your CRM identifies customers who purchased training access. Your payment processor handles course purchases. Your single sign-on service eliminates separate login credentials. Document the specific data that flows between each system and your LMS, including direction (one-way or two-way sync) and frequency (real-time or nightly batch).

Your integration map becomes a technical specification for your IT team:
Required Integrations:
1. HR System (BambooHR)
- Data: Employee name, email, department, hire date
- Direction: One-way to LMS
- Frequency: Nightly sync
- Owner: IT Lead
2. CRM (Salesforce)
- Data: Customer contact info, purchase history
- Direction: Two-way
- Frequency: Real-time
- Owner: Sales Operations
3. SSO (Okta)
- Data: User authentication
- Direction: Two-way
- Frequency: Real-time
- Owner: Security Team
Confirm that your LMS vendor supports native integrations for your key systems or provides API documentation for custom connections.
Step 4. Test, launch, and refine your LMS
Your lms implementation checklist reaches its critical testing phase before any learner touches the system. You prevent launch disasters by running structured quality assurance, executing a controlled rollout, and building feedback loops that catch problems early. Testing reveals broken integrations, confusing workflows, and missing content before they damage your credibility with users.
Run comprehensive QA testing
You start by creating test scenarios that mirror real user workflows. Your QA team should test every core function like user login, course enrollment, content playback, assessment completion, certificate generation, and reporting. Document each test case with expected results so you can verify the system behaves correctly.

Assign different testers to role-based scenarios. Have one tester act as a learner completing a certification path. Another plays an administrator enrolling users and pulling reports. A third tester simulates your manager role reviewing team progress. This approach catches permission errors and workflow gaps that single-user testing misses.
Your testing checklist should include:
Core Functions:
□ User authentication (SSO, standard login)
□ Course enrollment (manual, automatic, self-service)
□ Content playback (SCORM, video, PDF)
□ Assessment completion and scoring
□ Certificate generation and delivery
□ Integration data flow (CRM, HR, payment)
□ Mobile responsiveness
□ Reporting accuracy
Execute a phased rollout
You reduce risk by launching to small user groups first instead of your entire organization at once. Start with a pilot group of 20 to 50 users who represent your broader audience. These early users test the system under real conditions and surface issues your QA team missed.
Choose pilot users who will provide honest feedback and tolerate minor problems. Avoid selecting only tech-savvy users because they don’t represent typical learners. Your pilot runs for two to four weeks while you collect feedback and fix critical bugs.
A phased rollout gives you time to resolve problems before they affect thousands of users and damage adoption rates.
Gather feedback and iterate
Build ongoing feedback channels after launch instead of treating implementation as a one-time event. Add a feedback button inside your LMS so users can report issues directly. Schedule weekly check-ins with administrators during the first month to understand pain points.
Track key metrics like login rates, course completion percentages, and support ticket volume. Compare these numbers against your original objectives from step one. When metrics fall short, investigate why and adjust your approach. Your implementation never truly ends because continuous improvement keeps your LMS aligned with changing business needs.
Keep your LMS rollout on track
Your lms implementation checklist gives you control over complexity that would otherwise derail your project. You prevent the common mistakes that cause missed deadlines and budget overruns by following a structured approach. Document your goals upfront, assign clear ownership to every task, plan your content and integrations in detail, then test thoroughly before launching to your full user base.
The checklist becomes your ongoing project management tool throughout the implementation and beyond. You refer back to it weekly to track progress, identify blockers, and adjust timelines when constraints change. Update it as you learn what works and what doesn’t, so your next phase or portal rollout goes even smoother.
Ready to see how Axis LMS makes implementation faster? Our platform includes built-in integration capabilities for major CRM and HR systems, drag-and-drop course building, and automated user management that reduces your setup time. Schedule an admin demo to explore how our implementation support helps you launch your training program on schedule and within budget.
